3D Anatomy Model
Add another dimension to your learning with fully-interactive educational male and female anatomical models.
Learning about the human anatomy has never been more fun!
Purchase
Our hip joint is a ball and socket joint. The ball refers to the head of the femur (the thighbone) and the socket refers to the acetabular notch, part of the hip bone. The term acetabular fracture is used for fractures in the socket of the hip joint.
Acetabular fractures are much less common than the fractures of the ball of the femur or other femoral fractures. According to some sources, only 10% of the total pelvic fractures are comprised of acetabular fractures. In this article, we will discuss some causes, treatments, and complications associated with acetabular fractures.
The hip joint is a large and significant joint of our body. It helps stabilize our bodies and transmits the weight of the torso to the legs. As mentioned above, it is a ball and socket type joint. The acetabulum forming the socket and the femur (head) forming the ball.
The bones making the joint are covered by a smooth and slippery articular cartilage that works to reduce the friction between the ball and socket. The joint’s stability or strength comes from the strong ligaments that attach one bone to the other. A lot of our important organs, vessels, and nerves are in close proximity to the pelvic bones and these viscera can get damaged due to an acetabular fracture.
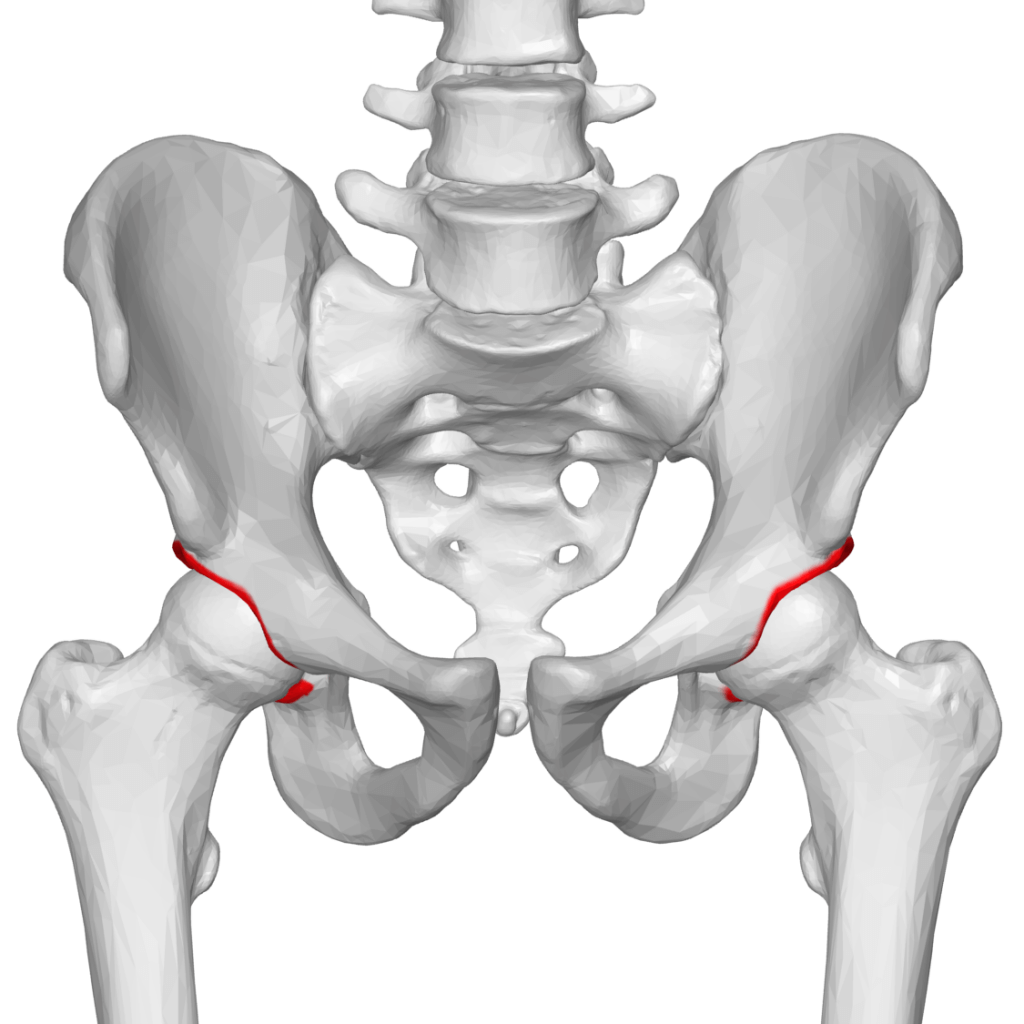
Symptoms of acetabular fracture do vary depending on the severity of the fractures. In some cases, there is only a minor crack in the acetabulum, and in other severe cases, the acetabulum might be broken away into several pieces. Like every other fracture in our body symptoms include:
Acetabular fractures occur when the head of the femur exerts an immense force on the socket, eventually breaking the socket. Auto-collisions (car crash) is a major source of this force. Your knee hitting the dashboard or steering wheel during the accident can put force on your acetabulum through the femoral head. It can also be caused by a direct fall on the sides of your hips, forcing the head of the femur into the socket breaking it.
Athletes playing contact sports may also experience this type of fracture, especially athletes playing Australian rugby, football, and gymnastics. Some risk factors include:
People with high-impact fractures almost always come to the hospital in an emergency. After stabilizing your pain, your doctor might take your history, perform a physical examination, and request some other diagnostic techniques to confirm if you have an acetabular fracture. These diagnostic techniques include:
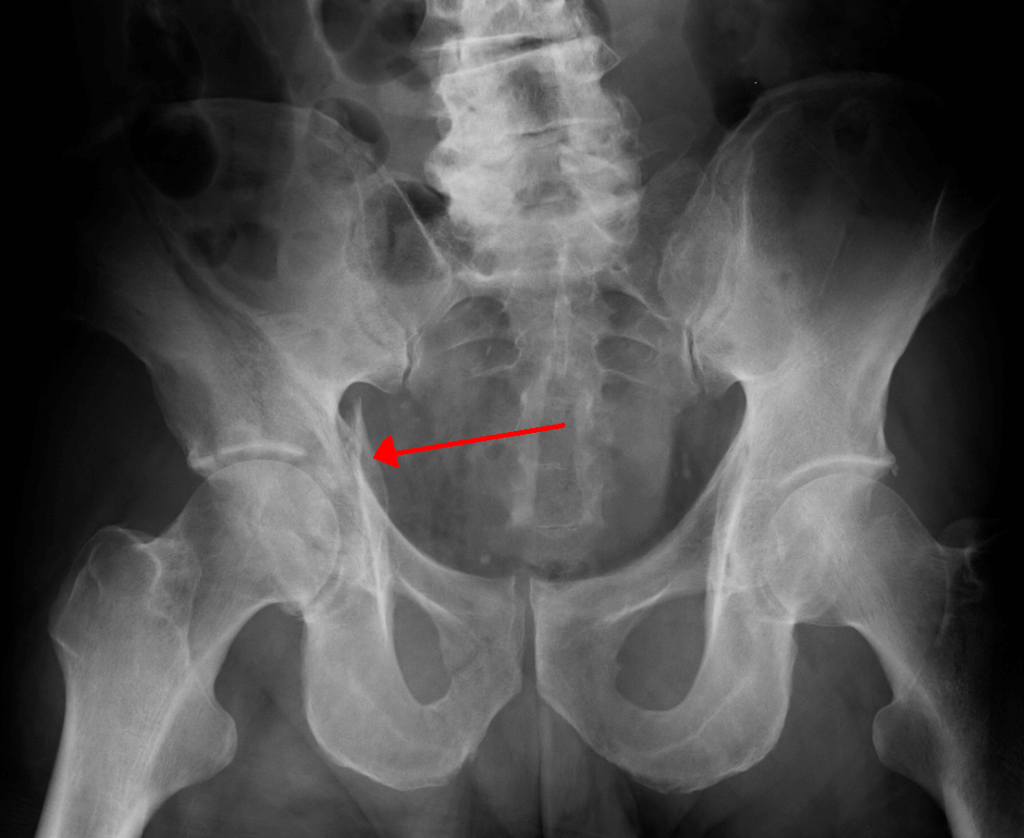
Treatment depends on the severity and pattern of your fracture along with your overall health status. There are a few treatment options available for acetabular fractures:
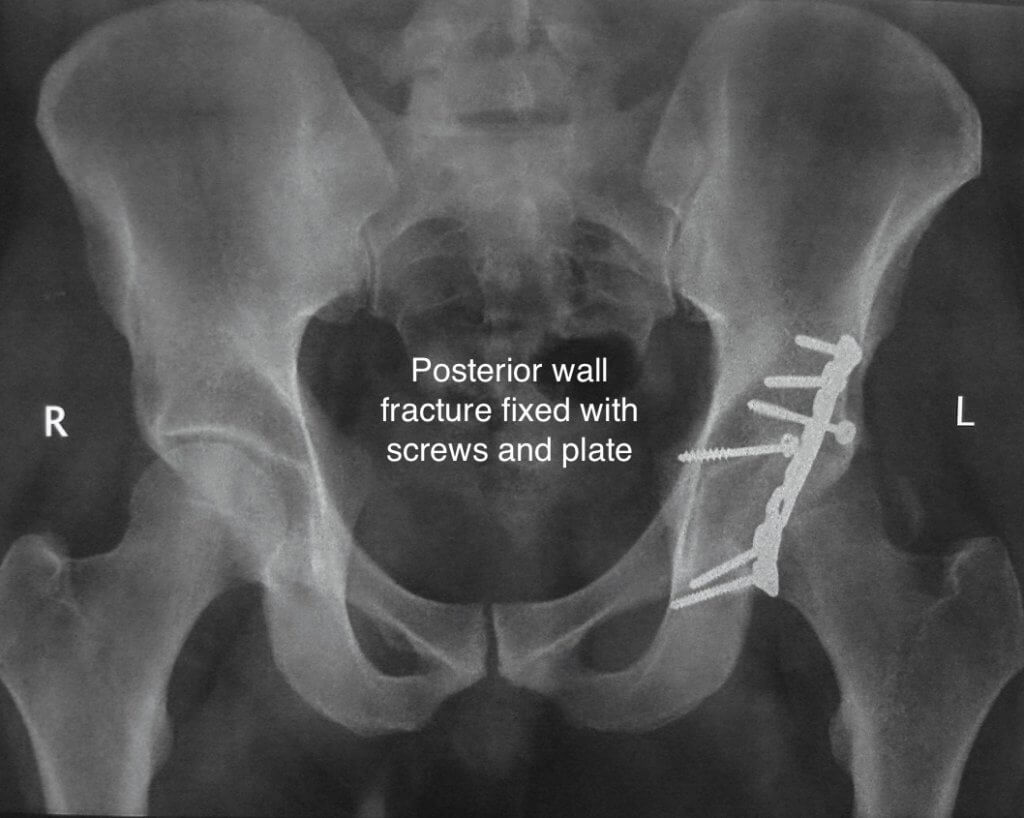
Acetabular fractures and their treatment can sometimes cause problematic complications. Some of these complications are:
You can prevent acetabular fractures by:
If you get into an accident or experience a high-impact fall on your legs resulting in severe pain, you need to get medical treatment right away. Along with the pain, you might experience swelling which might be increasing with time. Your doctor will treat you for the pain first and then manage the fractures you had.
Your recovery period depends on the severity of the injury you had. In case of minor fractures, you would be advised to rest for some time and then start doing light movements. However, in case of severe fractures, you would need to take bed rest for a longer period of time and along with other therapies. Most of the people recover fully and enjoy a healthy life.
Contributed and/or Updated by Jeffrey M. Smith, MD, Robert P. Dunbar, MD, Jason A. Lowe, MD, Jason D. Provus, MD
· Acetabular Fractures by OrthoInfo - https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/acetabular-fractures/
The content shared in the Health Literacy Hub website is provided for informational purposes only and it is not intended to replace advice, diagnosis, or treatment offered by qualified medical professionals in your State or Country. Readers are encouraged to confirm the information provided with other sources, and to seek the advice of a qualified medical practitioner with any question they may have regarding their health. The Health Literacy Hub is not liable for any direct or indirect consequence arising from the application of the material provided
