3D Anatomy Model
Add another dimension to your learning with fully-interactive educational male and female anatomical models.
Learning about the human anatomy has never been more fun!
Purchase
Sinuses are defined as hollow air-filled cavities present within bones or other tissues. The more commonly known sinuses are the ones present in the bones of the face and skull – the paranasal sinuses. As the name suggests these sinuses are present within the bony structure surrounding the nasal cavities and are present bilaterally (on each side).
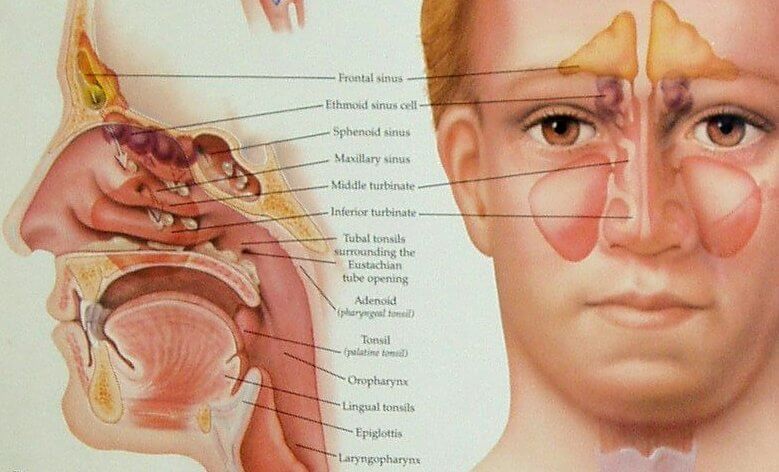
There are four paired paranasal sinuses that are named according to the bone they are situated in:
Frontal sinuses
Maxillary sinuses
Sphenoidal sinuses
Ethmoidal sinuses
The frontal sinuses are present in the frontal bone. You can think of them as air pockets present above the eyebrows on each side of the midline. These sinuses are the most superior in position and are triangular in shape. The frontal sinuses are irregular in their size and in most people the left frontal sinus is dominant.
For the understanding of the drainage system of the sinuses, you should take note of the following information. The nasal cavity is divided into three sections due to the presence of nasal bony projections. From the most superior to inferior – the superior, middle, and inferior nasal meatus. The frontal sinuses drain into the middle nasal meatus of the nasal cavity via the frontonasal duct.
The frontal sinuses are innervated (nerve supply) by the supraorbital nerve (a sub-branch of trigeminal nerve CN V) and their blood supply is via the anterior ethmoidal artery (a branch of the internal carotid artery).
The maxillary sinuses are the largest pair of paranasal sinuses. They are located in the maxilla (cheekbone) below the orbits (eyes) and at each side of the nasal cavities. The roots of the upper molar teeth make the floor of these sinuses. They drain in the middle nasal meatus at the place of drainage of the frontal sinuses – the semilunaris hiatus (a semicircular opening).
The maxillary sinuses are supplied by the branches of the superior alveolar artery (branch of the maxillary artery). The nerve signals from the maxillary sinuses are carried by the superior alveolar nerves (a branch of CN V). the maxillary sinuses are possible destinations for the spread of infection from the frontal sinuses due to their connection at the semilunaris hiatus.
The sphenoidal sinuses are located, approximately, at the level of the frontal sinuses in the sphenoid bone. They drain into the superior nasal meatus in an area called the spheno–ethmoidal recess. This recess is located just above and back of the upper part of the nose.
The nerve supply is carried by the posterior ethmoidal nerves (a sub-branch of CN V) and branches of the maxillary nerve. The blood to the sphenoidal sinuses is supplied via the pharyngeal branches of the maxillary artery.
There are three pairs of ethmoidal sinuses located within the ethmoid bone—the anterior, posterior, and middle ethmoidal sinuses. They are present just below the frontal bone (forehead) and medial to the eyes. The ethmoidal sinuses are a group of small ethmoidal air cells. These air cells are smaller sinuses collectively termed as the ethmoidal sinuses.
The anterior and middle ethmoidal sinuses drain in the middle meatus of the nasal cavity. The posterior ethmoidal sinuses open into the lateral walls of the superior nasal meatus. They are innervated by the anterior and posterior ethmoidal nerves (branches of the nasociliary nerve). The arterial supply is carried by the anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries.
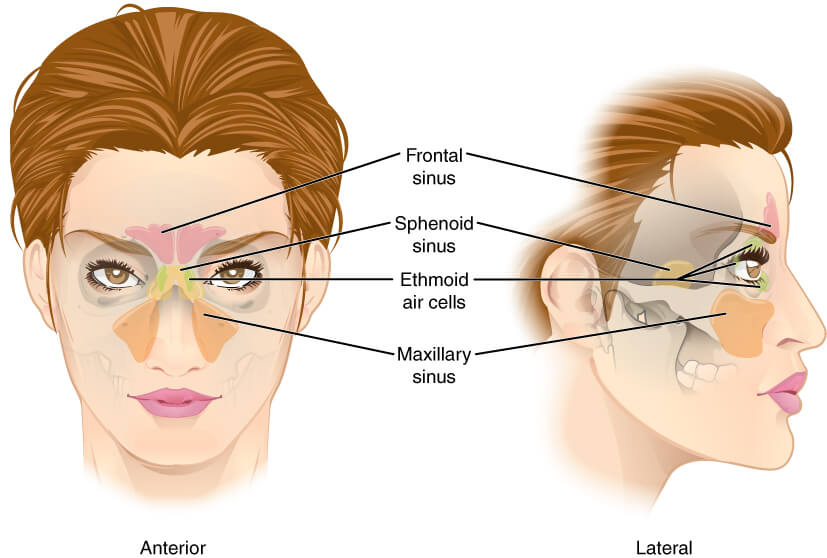
These sinuses help circulate the breathed air in and out of the nasal cavities and play various other roles including:
– Lightening of the head
– Increasing resonance of the voice i.e., deepening of the voice
– Humidifying the inspired air
– Supporting the immune system
– Runny nose
– Stuffy nose
– Facial pain, pressure, or heaviness
– Headache
– Cough
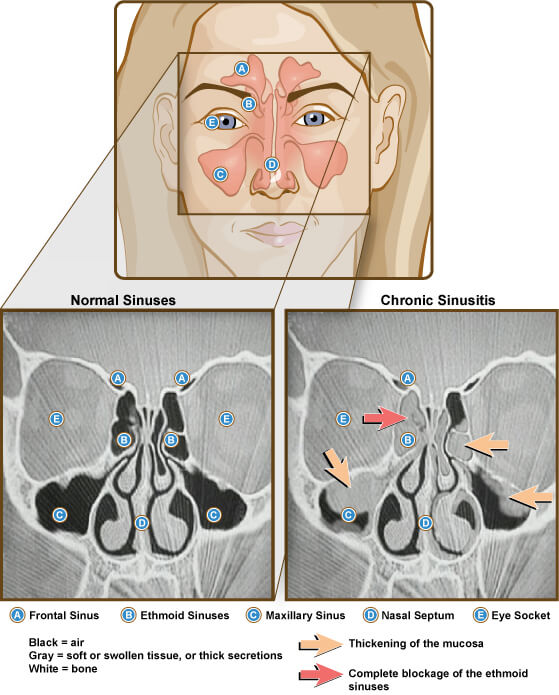
Chronic Sinusitis is a long persisting infection of the sinuses. It can be associated with other diseases like asthma and is common in people having allergies. Usually, supportive and preventive treatment is opted i.e., inhaling steam, wearing masks and avoiding dusty places, and the use of over-the-counter medications (NSAIDs). Steroidal therapy and surgery are sometimes used for the treatment of chronic cases of sinusitis.
The sphenoidal sinuses are closely related to the pituitary gland and provide a way to access the pituitary gland for surgical procedures. It allows less invasive surgery for the treatment of pituitary pathologies especially pituitary adenomas.
The content shared in the Health Literacy Hub website is provided for informational purposes only and it is not intended to replace advice, diagnosis, or treatment offered by qualified medical professionals in your State or Country. Readers are encouraged to confirm the information provided with other sources, and to seek the advice of a qualified medical practitioner with any question they may have regarding their health. The Health Literacy Hub is not liable for any direct or indirect consequence arising from the application of the material provided.
