3डी एनाटॉमी मॉडल
पूरी तरह से इंटरैक्टिव शैक्षिक पुरुष और महिला शारीरिक मॉडल के साथ अपने सीखने में एक और आयाम जोड़ें।
मानव शरीर रचना के बारे में सीखना इतना मजेदार कभी नहीं रहा!
खरीदना
The brachial plexus is an intricate network of nerves in the neck and shoulder that carries signals for movement and sensation from the spinal cord to the arms and hands. The brachial plexus consists of several parts: trunks, roots, cords, branches, and divisions.
All the nerves in the brachial plexus come from the spinal cord. Thus any severe brachial plexus injury affects the spinal cord as well.
Nerves originating from the neck portion of the vertebrae (cervical vertebrae) are known as cervical nerves. These nerves divide into 2 divisions that supply the front and the back of the body (anterior and posterior rami respectively).
The brachial plexus begins as roots of the cervical and thoracic anterior rami nerve fibers. It includes the fifth, 6th, 7th, 8th, and first thoracic vertebrae.
All of the brachial plexus roots combine to form brachial trunks as it proceeds down the neck.
All of these trunks are further divided into two divisions (dorsal and ventral). The dorsal division supplies the back of the upper limb, while the ventral supplies the front of the upper limb. The trunks divisions join to form brachial plexus cords.
The nerve roots of the brachial plexus have branches that supply muscles of the neck and shoulder:
Branches of the trunks only originate from the upper trunk of the plexus, which gives off two further branches:
Other than the brachial plexus branches, the upper limb has innervation from other cervical nerve fibers
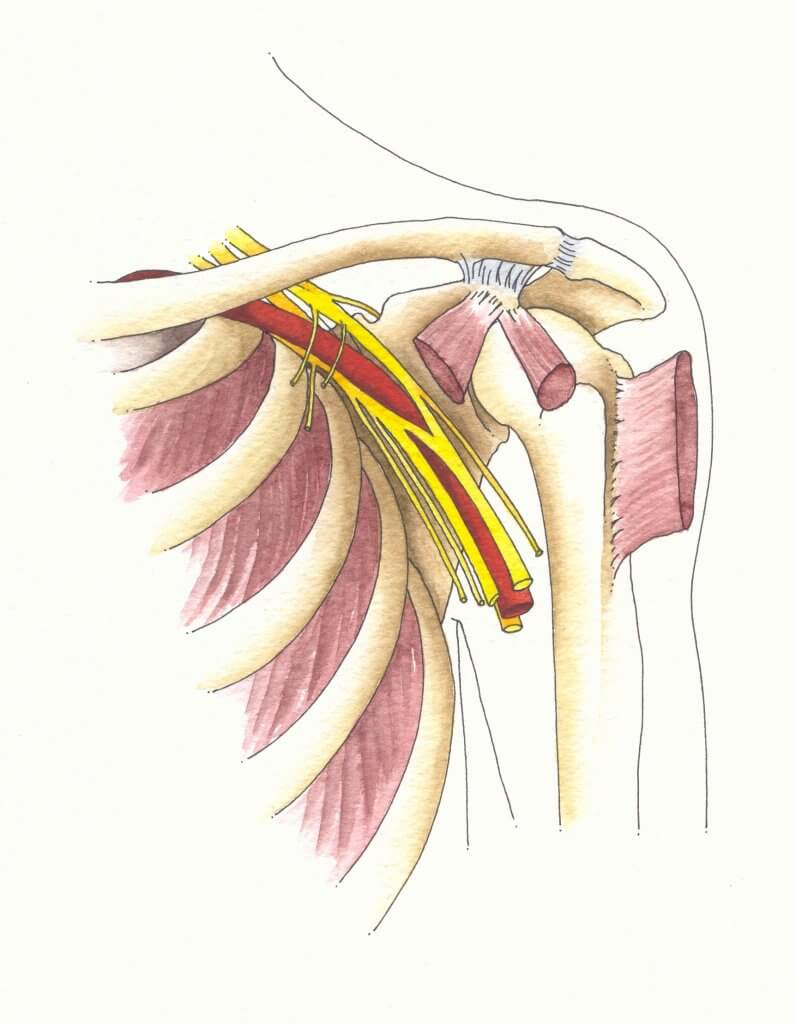
ब्रेकियल प्लेक्सस की कई चोटें विभिन्न स्थितियों के लिए जिम्मेदार हैं:
In the brachial plexus, there’s a point at the upper trunk referred to as the Erb’s point, it is where six nerves meet. Any injury to the upper trunk of the brachial plexus causes Erb’s paralysis. The mainly involved nerves in Erb’s paralysis are branches originating from the fifth and 6th cervical vertebrae.
The most commonly paralyzed muscles in this condition are deltoid, bicep brachii, brachioradialis, and brachialis muscles.
In Erb’s palsy, the arms tend to hang on the sides close to the body and are turned inwards such that the hand appears as if the individual is asking for a tip. This appearance is called the policeman’s or waiter’s tip appearance of the hands.
Serratus anterior nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus. In serratus anterior nerve injury, a person cannot raise or flex their arm above 90 degrees or raise it overhead because the serratus anterior muscle is a major participant in this movement.
Causes of this injury include :
The most prominent feature of this injury is the winging of the कंधे की हड्डी. Winging of the scapula is the abnormal prominence of the scapula bone. In the normal anatomical body, the कंधे की हड्डी is kept close to the chest wall through muscles that pull it against the thoracic wall. (One of these muscles is serratus anterior)
Serratus anterior nerve injury can also cause disability in punching and pushing actions. During the pushing attempts, winging of the scapula becomes very prominent.
This type of paralysis is due to injury to the lower trunk of the brachial plexus. Physical trauma to the arm, such as a sudden pull of the arm to the side, a fall from height, or pulling on a baby’s arm too hard during birth injury can be causes of this paralysis.
The mainly involved nerves in Klumpke’s paralysis are nerves originating from the 8th and first thoracic vertebrae.
Muscles paralyzed in this condition are the hand, forearm, and finger muscles. Kulumke’s paralysis causes a claw-hand appearance due to hyperextension of the hand and finger joints following muscle paralysis.
Other changes that can also occur include:
The skin with sensory problems is relatively warmer and also drier than the parts of the skin due to sweating loss and sympathetic activity loss. Long-standing Klumpke’s paralysis causes scaliness or dryness of the skin, easy cracking of the finger and nails, and a decrease in the size of the finger pulps.
हेल्थ लिटरेसी हब वेबसाइट पर साझा की गई सामग्री केवल सूचना के उद्देश्यों के लिए प्रदान की जाती है और इसका उद्देश्य आपके राज्य या देश में योग्य चिकित्सा पेशेवरों द्वारा दी जाने वाली सलाह, निदान या उपचार को प्रतिस्थापित करना नहीं है। पाठकों को अन्य स्रोतों के साथ प्रदान की गई जानकारी की पुष्टि करने और अपने स्वास्थ्य के संबंध में किसी भी प्रश्न के लिए एक योग्य चिकित्सक की सलाह लेने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया जाता है। स्वास्थ्य साक्षरता हब प्रदान की गई सामग्री के उपयोग से उत्पन्न होने वाले किसी भी प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष परिणाम के लिए उत्तरदायी नहीं है।
