髄膜の構造と機能に関する5つの重要な事実
The human brain is a very sensitive structure in terms of trauma and injury. Several protective features help keep the brain in a protective environment. One of these features is the meninges.
髄膜についての最も興味深い事実を見てみましょう。
1. The meninges are sheet-like covering of the brain that help keep the Central Nervous System ( CNS ) in place and stabilise it. The meninges are also found within the spinal canal in the spinal cord.
2.脳と脊椎では、髄膜は神経組織に保護と栄養素を提供する脳脊髄液(CSF)の循環も調節します。
3. Specialised cells (meningeal cells) in the meningeal tissue are responsible for a protective mechanism called meningeal immunity that controls and intervene in the presence of a pathogen-mediated infection.
4. What we refer to as “the meninges” represents three independent layers of tissue located in the skull (cranial cavity) and surrounding the spinal cord characterised by a unique structure and role. The dura mater, the outermost layer, consists of two sheets of connective tissue lining the interior surface of the cranial cavity. The arachnoid layer, the middle layer, is made of non-vascularised connective tissue. The pia mater, the innermost layer, is a very thin sheet that covers the brain surface and is highly vascularised.
5. The space between the arachnoid and pia maters is known as “subarachnoid space”. In this region where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates, there is a particular compartment (subarachnoid cisterns) characterised by the accumulation of CSF (pools or cisterns) to provide the brain with nutrients, enable solute exchange, and offer mechanical and functional support to the brain.
この記事では、この脳保護層に関連する構造、機能、および最も一般的な病気について詳しく説明します。
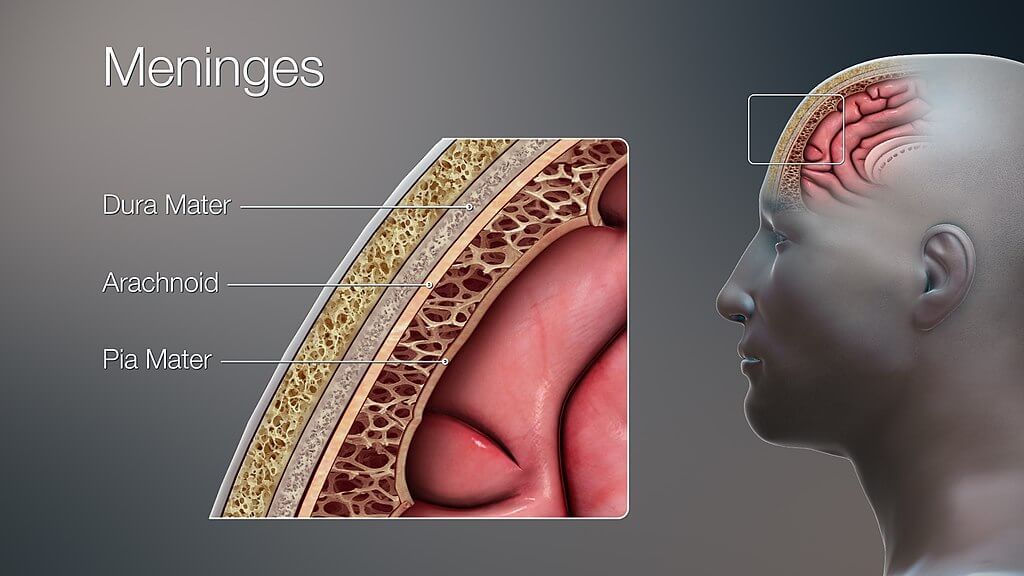
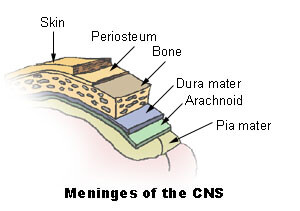
構造
Our brain is suspended or floating in the CSF and covered by 三つ 髄膜の層:
髄膜は脳と脊髄の両方を包み込み、それらを取り巻く骨、すなわち頭蓋骨と脊柱からそれらを分離します。髄膜はさらに地形的に分類されます 頭蓋 と 脊椎 meninges. There are three clinically important spaces bounded by the meninges, they are the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. The arachnoid and 軟膜 とも呼ばれます leptomeninges;その理由は、これら2つの層の間にCSFが存在するためです。
Apart from its mechanical function, the meninges act to support the blood vessels and form a continuous cavity for the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
硬膜
The 硬膜 最外髄膜層です。それは密な不規則な結合組織で構成されており、2つの層で構成されています:
- The 骨膜 layer: the superficial layer that is attached to the inner table of the bony skull.
- The 髄膜 layer: lies on top of the arachnoid mater.
These two layers are inseparable except in places where they separate to envelop large veins known as dural venous sinuses. In these above-mentioned places, the 硬膜 projects inward towards the brain tissue forming a fibrous partition. These partitions are within the 頭蓋骨 とは次のとおりです。
- Falx cerebri: The largest of the three septa. It is a midline structure that separates the brain hemispheres, and it houses the 上矢状静脈洞 と 下矢状静脈洞 venous sinuses.
- テントリウム cerebelli: This spans in a horizontal plane from the inner surface of the occipital bone. It separates the superiorly lying brain tissue (cerebrum) from the inferiorly lying portion (cerebellum) and contains the 真っ直ぐ, 横、 と 優れました 矢状 sinuses. This structure also divides the intracranial space into テント上 (above the partition) and テント下 (below the partition) compartments.
- 小脳鎌: It projects from the midline of the occipital bone, separating the hemispheres of the cerebellum and housing the 後頭 副鼻腔。
- Diaphragma sellae: It is a flat membrane surrounding the stalk of the pituitary gland and forms the outer covering (roof) for where the pituitary gland sits. The anterior and posterior 海綿間 副鼻腔がここにあります。
の脊髄部分 硬膜 対照的に、骨膜層はありません。この違いは、頭蓋骨とは異なり、脊柱が独自の骨膜層を持っているという事実に起因する可能性があります。
クモ膜
この髄膜の層は硬膜と 軟膜。 The 潜在的な 硬膜とくも膜の間の空間は、 硬膜下 (硬膜に深く)そしてくも膜との間の空間 軟膜 と呼ばれます くも膜下 (deeper to arachnoid) space. The latter is a true space that contains the Cerebrospinal fluid in it. This space is also the location of all the cerebral arteries and veins. The 脊椎 クモ膜の問題は、頭蓋のクモ膜の母体の継続です。
クモ膜は硬膜に付着しており、 軟膜 さまざまな場所で。硬膜との付着部位には、キノコのような突起があります。 クモ膜 造粒. These granulations protrude into the dural venous sinuses and enable the continuous flow of CSF from the subarachnoid space to the venous system.
軟膜
これは、脳の輪郭にぴったりと沿った、薄くて血管の多い層です。脳のいくつかの血管はこの層に関連していますが、それらは 軟膜 とは別々に名前が付けられていません。 The 軟膜 functions to physically separate the nervous tissue from the vasculature present in the subarachnoid space. It also increases the efficacy of the blood-brain barrier, a vital component for the brain tissue to stay healthy.
脊椎 軟膜 closely attaches to the spinal cord and gives off a fibrous projection at the end of the spinal cord – the 終末線維。
髄膜スペース
前に説明したように、3つの髄膜層はそれらの間に潜在的なスペースがあり、次のとおりです。
These spaces are of much clinical importance in traumatic injuries to the head. Blood can leak into these spaces pathologically and cause haemorrhages which can be fatal.
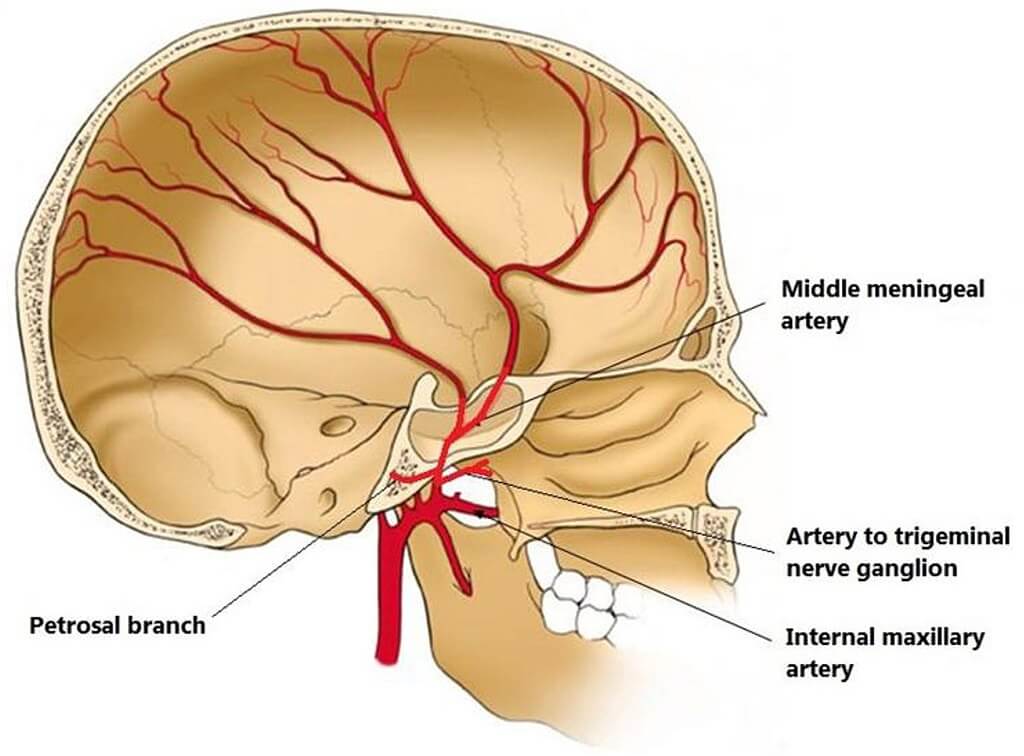
神経血管供給
髄膜は、 三叉神経 (Fifth cranial nerve). The blood supply to the meninges is from the branches of the 頚動脈 と 脊椎 動脈。
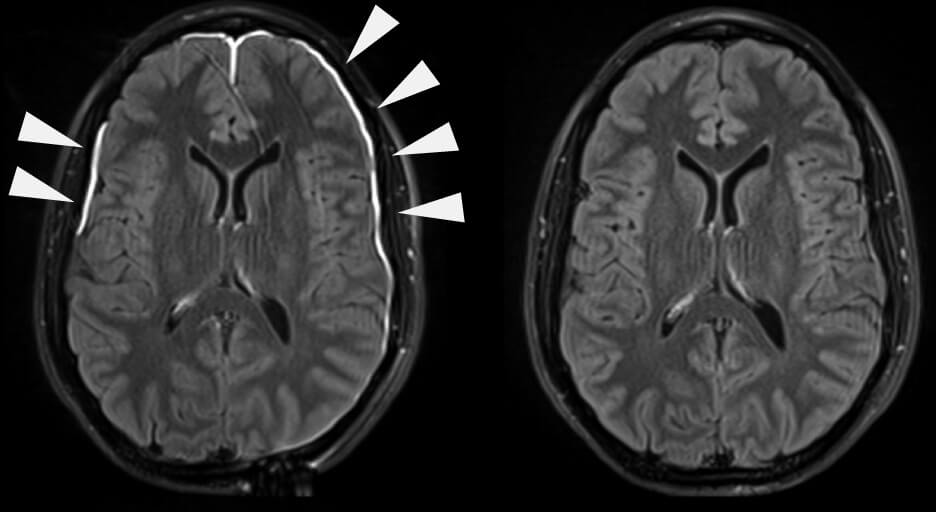
臨床的関連性および関連する障害
髄膜炎
The 炎症 (swelling) of the meninges is termed 髄膜炎。これは最も一般的には細菌によって引き起こされますが、ウイルスによって引き起こされる可能性があり、薬物によって引き起こされることさえあります。 バクテリア 髄膜炎は、最も一般的に2つのバグ(病原体)によって引き起こされます: ナイセリア 髄膜炎菌 と 連鎖球菌 肺炎。一方、ウイルス性髄膜炎は、最も一般的には エンテロウイルス.
髄膜炎 通常、原因を確認した後、抗生物質と抗ウイルス薬で治療されます。しかし、未治療では、深刻な合併症に向かって進行する可能性があります。 brain herniations、など。
髄膜炎の詳細については、 これ 記事。
硬膜外および硬膜下血腫
A 血腫 is blood pooling or collection. Increased pressure in the skull due to this build-up causes a rapid increase in the intracranial pressure due to the skull being a closed cavity. On CT scans they are seen as crescent-shaped formations. There are two types of haematomas:
- 硬膜外 血腫–動脈血は頭蓋冠(頭蓋骨)と骨膜層の間に蓄積します 硬膜。最も一般的に負傷する血管は、頭の側面(寺院)を走る中硬膜動脈です。
- 硬膜下 Haematoma – occurs when blood accumulates between the dura and the arachnoid mater. It is caused by venous blood pooling and usually involves the rupture of cerebral veins as they empty into the dural venous sinuses.
Another classification of subdural haematomas is based on the timeframe of their formation i.e., acute or chronic subdural haematomas. Acute haematomas are caused by sudden forceful brain injuries while chronic haematomas can result from a weak or small injury and are usually due to another underlying cause. Haematomas can be fatal if they are not treated immediately.
- オリバージョーンズ。解剖学を教えてください。神経解剖学;中枢神経系の構造;髄膜。
- オーギュスタン、GJ、フィッツパトリック、D。(2004)。神経科学(第3版)。米国マサチューセッツ州サンダーランド:Sinauer Associates
- Blumenfeld、H。(2018)。臨床例による神経解剖学(第2版)。マサチューセッツ州サンダーランド:シナウアー。
- ヘインズ、DE、ミハイロフ、GA(2018)。基本的および臨床的応用のための基本的な神経科学。ペンシルベニア州フィラデルフィア:エルゼビア。
- ヘインズ、DE(2014)。臨床的文脈における神経解剖学:構造、切片、システムおよび症候群のアトラス(第9版)。ペンシルベニア州フィラデルフィア:リッピンコットウィリアムズ&ウィルキンス。
- Mancall、EL、Brock、DG、&Gray、H。(2011)グレイの臨床神経解剖学:臨床神経科学の解剖学的基礎。ペンシルベニア州フィラデルフィア:エルゼビア。
- Moore、KL、Dalley、AF、およびAgur、AMR(2014)。臨床指向の解剖学(第7版)。ペンシルベニア州フィラデルフィア:リッピンコットウィリアムズ&ウィルキンス。
- ネッター、F。(2019)。人体解剖学のアトラス(第7版)。ペンシルベニア州フィラデルフィア:サンダース。
- パテスタス、マサチューセッツ州、ガートナー、LP、およびパテスタス、マサチューセッツ州(2009年)。神経解剖学の教科書。英国オックスフォード:ブラックウェル出版。
- スネル、リチャードS.(2018)臨床神経解剖学(第8版)。フィラデルフィア:Wolters Kluwer Health / Lippincott Williams&Wilkins
- スタンディング、S。(2016)。グレイの解剖学(第41版)。エジンバラ:Elsevier Churchill Livingstone
Health Literacy Hub Webサイトで共有されるコンテンツは、情報提供のみを目的として提供されており、州または国の資格のある医療専門家が提供するアドバイス、診断、または治療に代わるものではありません。読者は、他の情報源から提供された情報を確認し、自分の健康に関して質問がある場合は、資格のある開業医のアドバイスを求めることをお勧めします。 Health Literacy Hubは、提供された資料の適用から生じる直接的または間接的な結果に対して責任を負いません。