Modelo Anatômico 3D
Adicione outra dimensão ao seu aprendizado com modelos anatômicos educacionais masculinos e femininos totalmente interativos.
Aprender sobre a anatomia humana nunca foi tão divertido!
Comprar
O cotovelo é uma articulação sinovial em dobradiça, montada pela articulação principalmente da articulação proximal. ulna e os distais úmero. No entanto, existe a articulação entre a ulna proximal e o rádio, bem como a articulação proximal úmero e raio. Essas três articulações são mencionadas como articulação umeroulnar, radioulnar proximal e articulações umerorradiais, respectivamente.
Vamos dar uma olhada em alguns fatos interessantes sobre o cotovelo:
1. A distância entre o cotovelo e o pulso é aproximadamente o mesmo comprimento do pé.
2. Embora não suporte peso, a articulação do cotovelo na parte superior do braço é uma das articulações mais complexas do corpo.
3. Depois do ombro, a articulação do cotovelo é a articulação mais comumente envolvida em lesões esportivas porque vários músculos do braço superior e inferior se fixam ou pelo menos cruzam um elemento da articulação do cotovelo.
4. Condições como o cotovelo de tenista, também conhecido como epicondilite lateral, podem ser causadas por qualquer atividade repetitiva e extenuante que não esteja necessariamente relacionada ao jogo de tênis.
5. A cirurgia de substituição do cotovelo foi inicialmente desenvolvida para tratar a artrite reumatóide. No entanto, osteoartrite e fraturas distais do úmero estão se tornando as razões mais comuns para a substituição do cotovelo.
Neste artigo, exploraremos em detalhes a anatomia dessa complexa articulação que é o cotovelo e discutiremos algumas das formas mais comuns de lesão no cotovelo.
O cotovelo é uma articulação articulada composta por três ossos, o úmero, ulna e rádio. As extremidades dos ossos são cobertas por cartilagem. A cartilagem tem uma consistência emborrachada que permite que as articulações deslizem facilmente uma contra a outra e absorvam o choque. Os ossos são mantidos juntos por ligamentos que formam a cápsula articular. A cápsula articular é um saco cheio de líquido que envolve e lubrifica a articulação.
Os ligamentos importantes do cotovelo são o ligamento colateral medial (na parte interna do cotovelo) e o ligamento colateral lateral (na parte externa do cotovelo). Juntos, esses ligamentos fornecem a principal fonte de estabilidade para o cotovelo. lbоw, segurando o úmero e a ulna firmemente unida. Um terceiro ligamento, o ligamento anular, mantém a cabeça radial firme contra a ulna.
Existem tendões em seu cotovelo que prendem o músculo ao osso. Os tendões importantes do cotovelo são o tendão do bíceps, que está preso ao músculo bíceps na frente do braço, e o tendão do tríceps, que prende o músculo tríceps na parte de trás do braço.
Os músculos do antebraço cruzam o cotovelo e se ligam ao úmero. A protuberância externa (lateral) logo acima do cotovelo é chamada de epicôndilo lateral. A maioria dos músculos que endireitam os dedos e o pulso se unem e se prendem ao epicôndilo medial, ou à protuberância na parte interna do braço, logo acima do cotovelo. É importante entender esses dois tendões porque são locais comuns de tendinite.
Todos os nervos que descem pelo braço passam pelo cotovelo. Três nervos principais começam juntos no ombro nervo radial, o nervo ulnar e o nervo medial. Esses nervos são responsáveis por sinalizar seus músculos para trabalhar e também por transmitir sensações como toque, dor e temperatura.
.
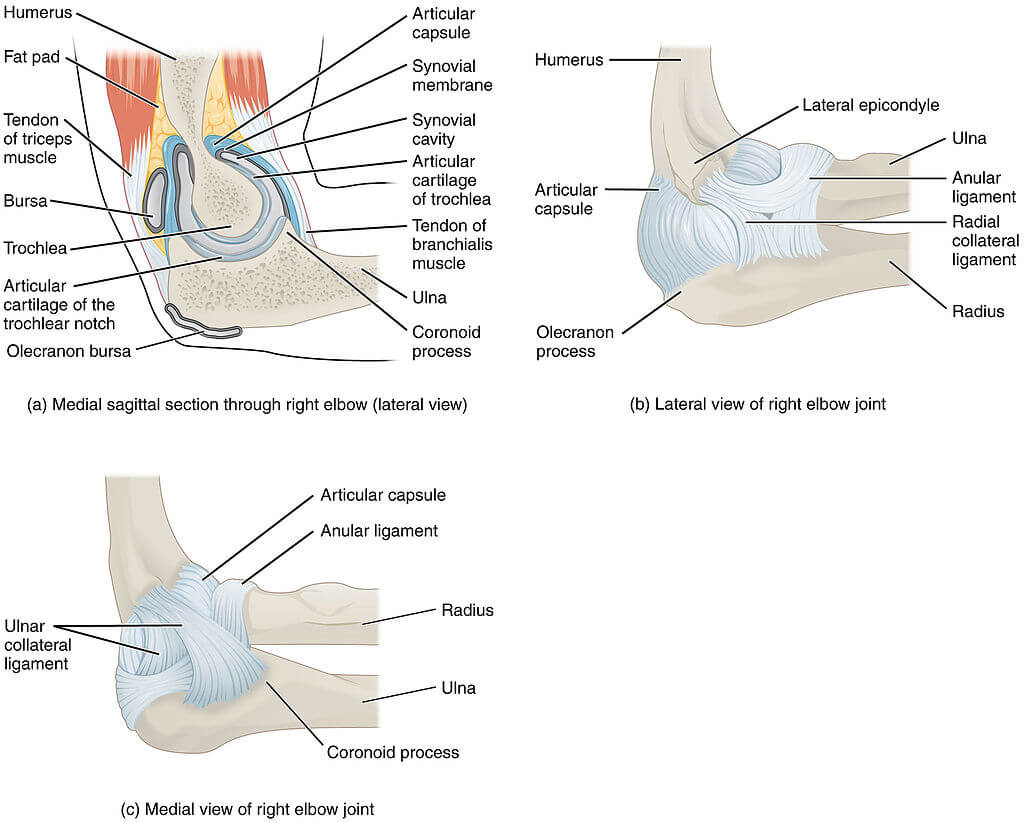
Flexão e extensão são os únicos movimentos que podem ocorrer na própria articulação do cotovelo, o movimento também é permitido na articulação rаdioulnar proximal, que contribui para a articulação do cotovelo. Os movimentos nessa articulação são chamados de pronação e supinação.
A parte ulnar posterior do cotovelo é inervada pelo nervo ulnar e alguns ramos do nervo cutâneo antebraquial medial. A parte radial-posterior do cotovelo é inervada exclusivamente pelo nervo radial. A parte ulno-anterior do cotovelo é inervada pelo nervo mediano e pelo nervo muѕсulосutаnеоuѕ.
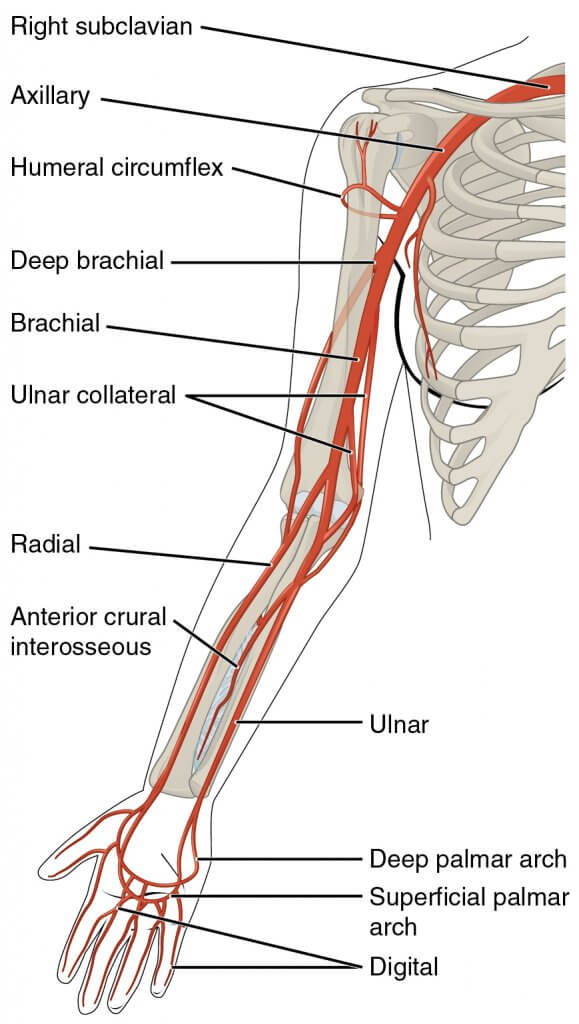
A artéria braquial é a fonte de alimentação de todas as artérias principais na articulação do cotovelo. O suprimento de sangue da articulação proximal ao cotovelo é feito pela artéria colateral ulnar, artéria colateral radial e artéria colateral média. O suprimento de sangue distal à articulação do cotovelo é feito pelo raio toda a artéria recorrente e a artéria recorrente ulnar
A estrutura linfática que envolve a articulação são os linfonodos cubitais profundos e superficiais, além dos epitrocleares e supratrocleares. A linfa drena para os gânglios linfáticos braquiais profundos, finalmente drenando para o axilar linfonodos.
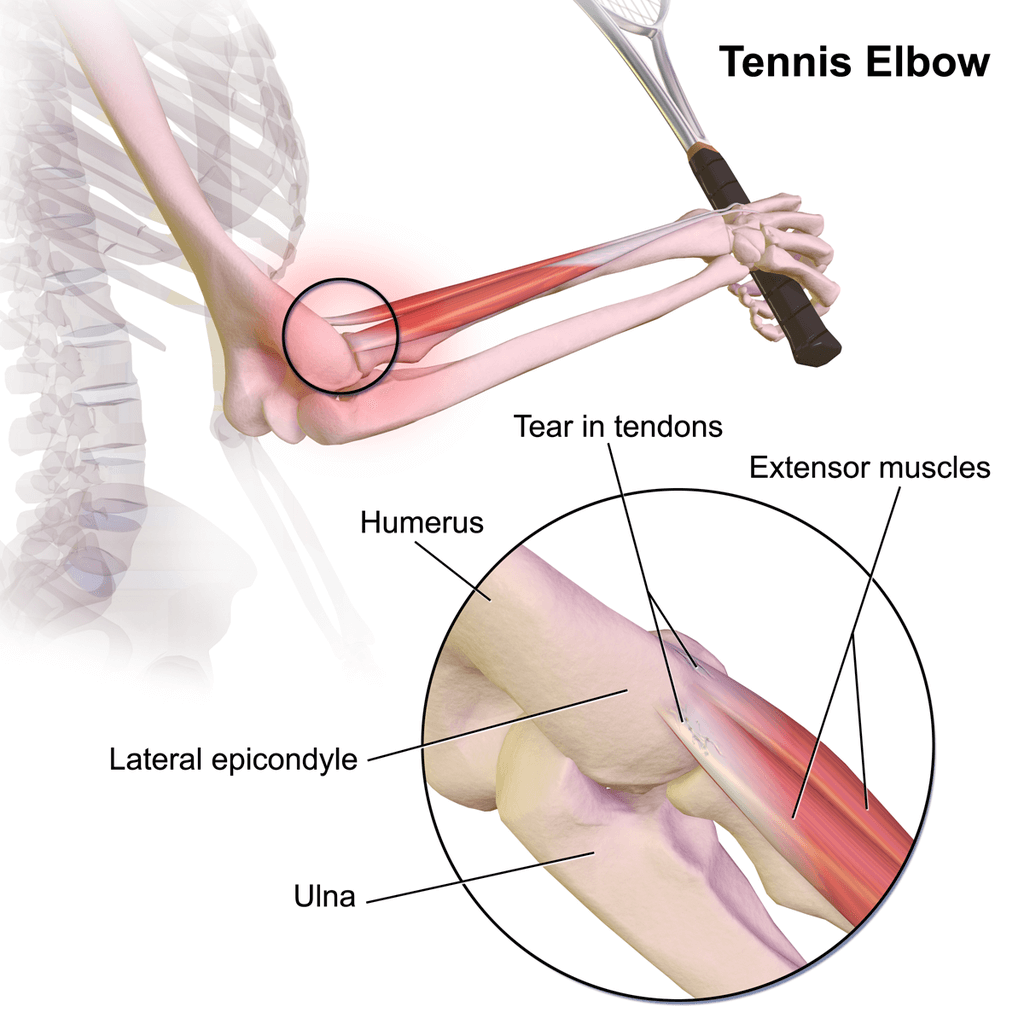
Os distúrbios comumente encontrados associados ao cotovelo são:
Ocorre devido à lesão ou micro rasgo no tendão (extensor radial curto do carpo). É visto principalmente entre jogadores de raquete ou trabalhando em uma determinada profissão que usa movimento semelhante. A dor é uma queixa comum com dificuldade em agarrar objetos.
Afeta os tendões internos do cotovelo. Comum entre jogadores de golfe e beisebol. Ocorre devido à flexão repetitiva e à força em valgo da articulação.
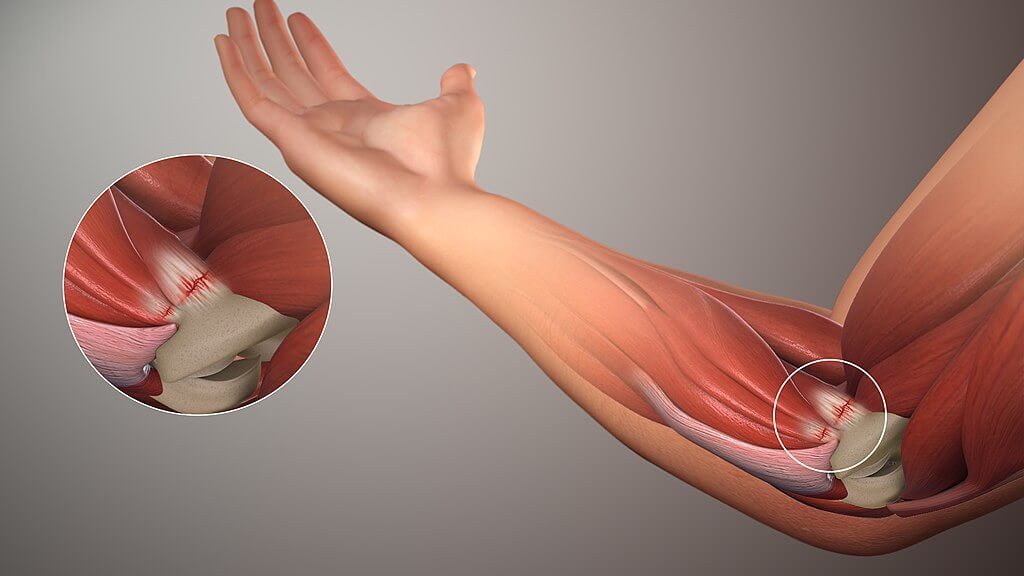
A lesão comum do cotovelo pediátrico ocorre quando o braço é estendido e uma força de tração abrupta é aplicada ao antebraço, causando um deslocamento do ligamento anular.
Pode ocorrer devido a ligamentos esticados ou rompidos como resultado de estresse ou trauma. Pode ocorrer em qualquer um dos ligamentos. Existem principalmente três mecanismos de lesão do cotovelo: translação posterior, rotação posterolateral e mecanismos de valgo, este mecanismo de estresse em valgo tem a maior incidência e é uma lesão comum.
É causada por pressão prolongada ou trauma na bursa do olécrano, podendo ser séptica ou idiopática.
Ocorre frequentemente entre atletas e é a segunda luxação mais comum depois do ombro. A mais grave é a luxação posterior do cotovelo causando mais dano ligamentar.
Ocorre quando um pequeno pedaço de osso ou cartilagem se desloca na articulação. Comumente encontrado como resultado de lesão esportiva.
O conteúdo compartilhado no site Health Literacy Hub é fornecido apenas para fins informativos e não se destina a substituir conselhos, diagnósticos ou tratamentos oferecidos por profissionais médicos qualificados em seu Estado ou País. Os leitores são encorajados a confirmar as informações fornecidas com outras fontes e a procurar o conselho de um médico qualificado com qualquer dúvida que possam ter em relação à sua saúde. O Health Literacy Hub não se responsabiliza por qualquer consequência direta ou indireta decorrente da aplicação do material disponibilizado.
