Descripción general
Neuropathy refers to any problem associated with nerves. Polyneuropathy is a condition in which multiple peripheral nerves are damaged. This condition is interchangeably called peripheral neuropathy.
Los nervios presentes fuera del cerebro y la médula espinal se llaman nervios periféricos. Mantienen una conexión entre el sistema nervioso central (SNC) y otras partes del cuerpo. En la polineuropatía, diferentes nervios del cuerpo se ven afectados simultáneamente y los nervios afectados pueden incluir:
- Sensory neuropathy – nerves responsible for sensation or feeling
- Motor neuropathy – nerves that transmit the signals to the muscles for movement of the body
- Sensorimotor neuropathy – involving both sensory and motor nerves
Polyneuropathy is seen in around 1% of the general population and 7% of the older population, with western countries being more affected. Hints are also there showing that females are more commonly affected than males.
In this article, we will review some clinical features of polyneuropathy, its causes, treatments, and preventions.
Tipos
Las neuropatías periféricas están presentes en muchas formas diferentes, por ejemplo, la neuropatía asociada con la diabetes (niveles altos de azúcar en la sangre) se denomina neuropatía diabética. Existen algunas clasificaciones generales para la polineuropatía:
- Neuropatía periférica simétrica crónica – neuropathies that develop over many months or years. They develop slowly and comprise most of the polyneuropathy cases.
- Mononeuropatías múltiples – damage to at least two separate nerve areas
- Neuropatía periférica simétrica aguda – sudden onset and damage to the nerves. It is a rare condition and the most commonly determined cause is the Guillain-Barre syndrome. It can precipitate to be fatal if not treated.
Síntomas
La polineuropatía puede presentarse en una variedad de formas con una amplia gama de síntomas. Los síntomas dependen de los nervios que están dañados o afectados junto con el área que estos nervios están irrigando. Las neuropatías sensoriales o motoras pueden presentarse como:
- Paraesthesia – burning or tingling along with the feeling of needles or pins
- Numbness
- Dificultad para mover brazos, piernas o pies
- Insomnia due to night-time pain
- Inability to feel pain, sense temperature change, etc.
- Pierna and foot ulcers – commonly associated with diabetes mellitus
- Recurrent infections
- Muscle spasms or twitching
Los síntomas asociados con la neuropatía de los nervios autónomos (parte del sistema nervioso autónomo) son:
- Unusual sweating
- Flushing of skin and heat intolerance
- Digestive issues
- Mareo
- Abnormal blood pressure or pulse problems
- Difficulty in breathing, or swallowing
Causas y factores de riesgo
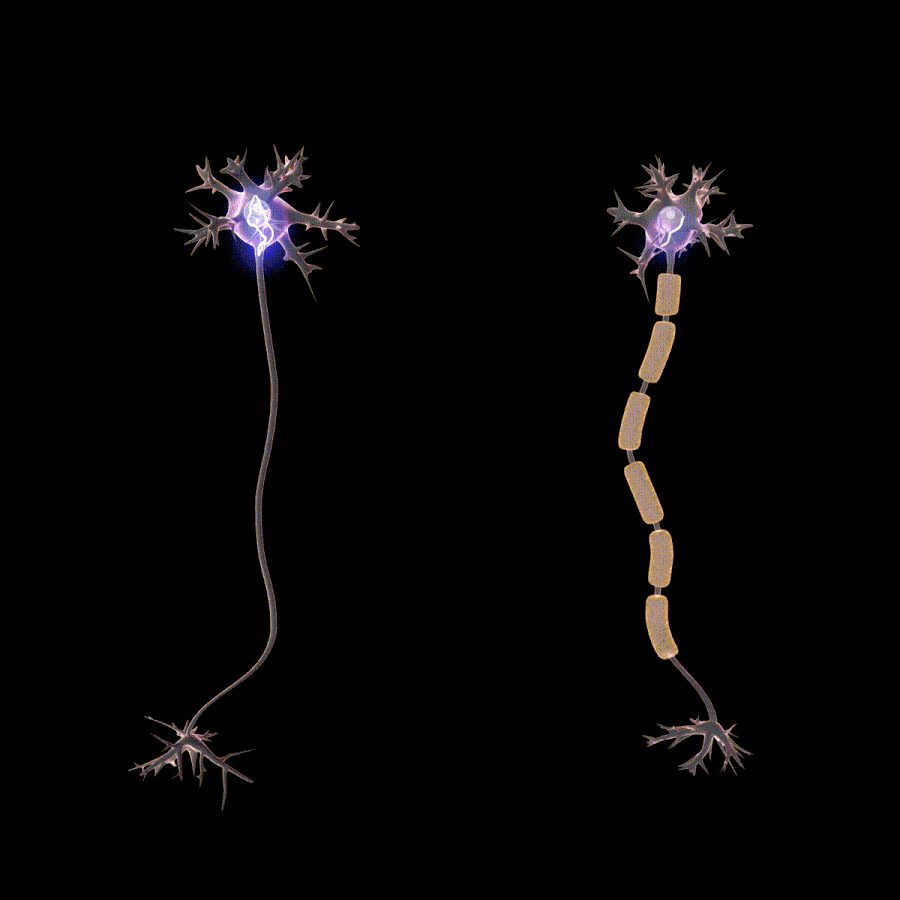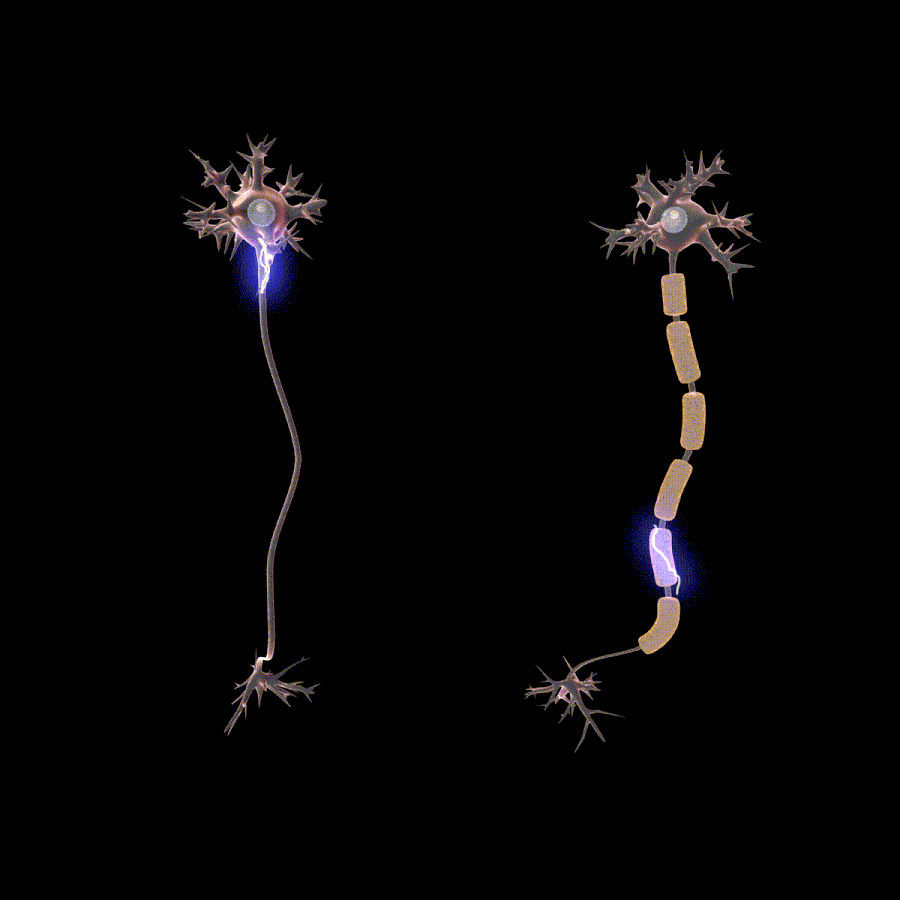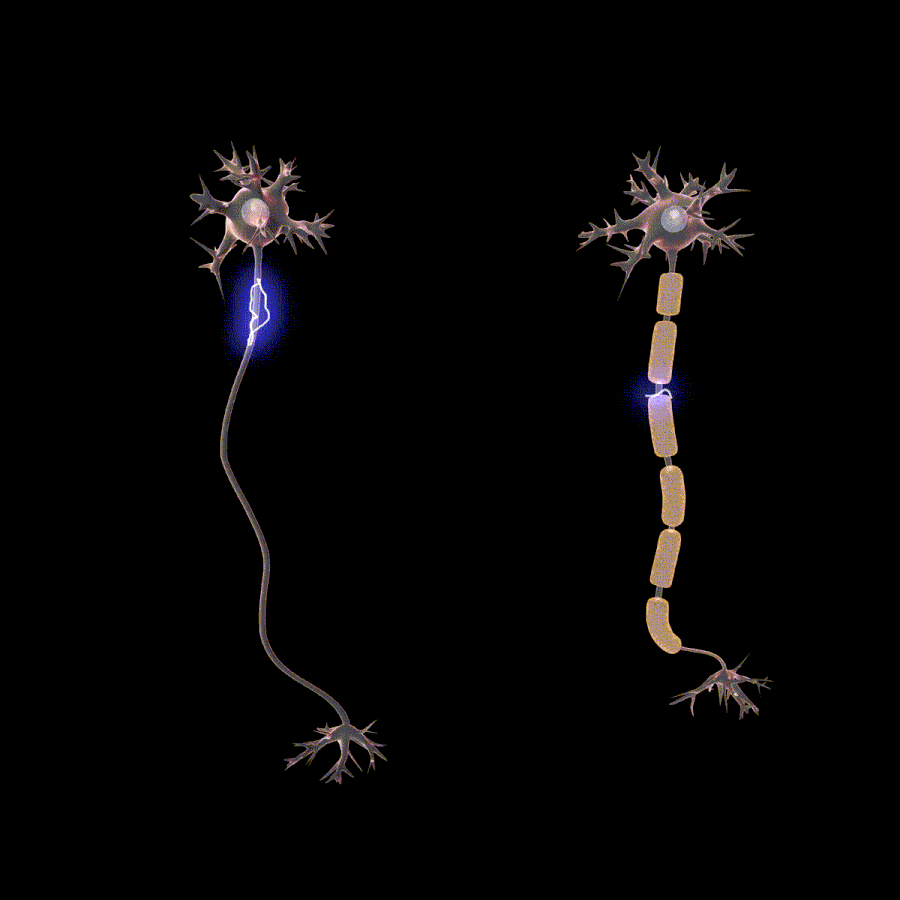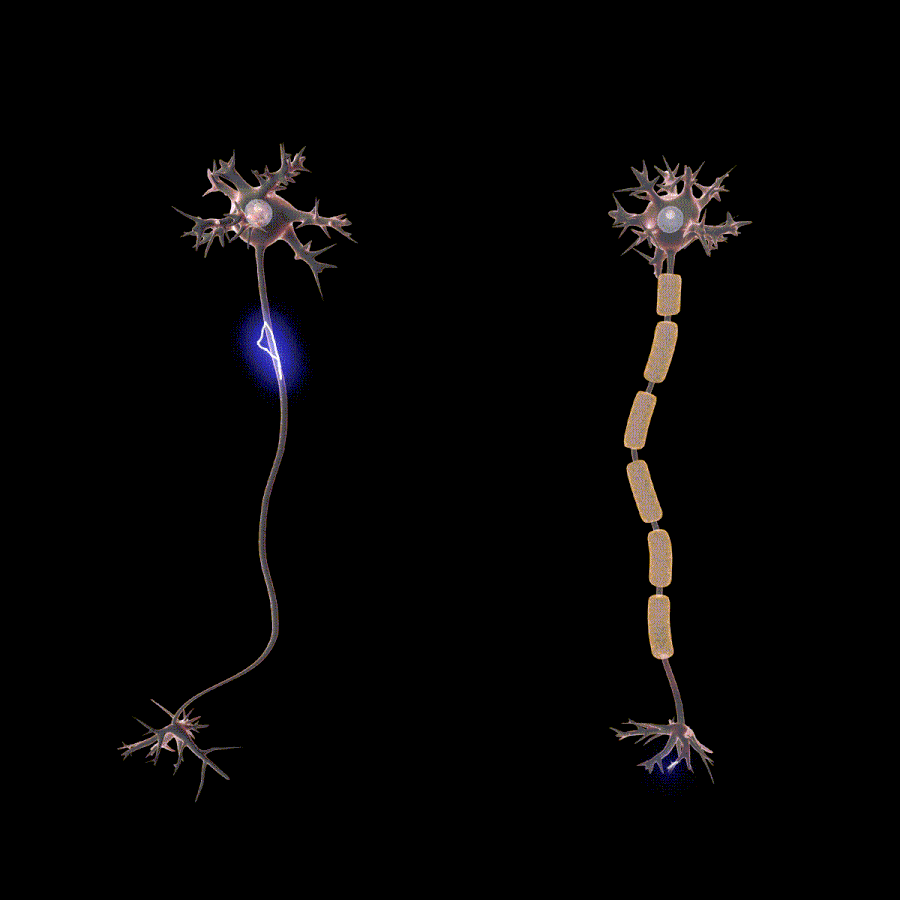
La polineuropatía es causada por daño al cuerpo de la célula neuronal o al axón. Una neurona es un término que se refiere a una célula nerviosa. El axón es la cola larga que transporta información y está unida al cuerpo celular. Las causas comunes son cambios anormales en el cuerpo celular, por ejemplo, exceso de azúcar, traumatismo físico en el cuerpo celular o el axón, etc. Algunas enfermedades y factores de riesgo asociados con la polineuropatía son:
- Diabetes – the most common cause of neuropathy is diabetes. The associated nerve damage is oftentimes called diabetic neuropathy. It is caused by uncontrolled blood sugar levels. This excess sugar can go into nerve cells and get trapped there causing damage to the cell and inducing neuropathy
- Alcohol abuso – excessive alcohol use causes several nutritional deficiencies like vitamin deficiencies. This can cause nerve tissue damage eventually damaging several nerves of the body
- Bacteriano o infecciones virales – certain bacteria or viruses attack and even live in the neurons of the body, eventually causing damage or cell death. These include bugs causing Lyme disease, Shingles, Herpes, hepatitis B or C, HIV, or Campylobacter
- Condiciones autoinmunes – people who have autoimmune disorders like Sjogren’s syndrome, Guillain-Barre syndrome (associated with Campylobacter), rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus can have an increased risk of developing neuropathies. In autoimmune disease, your immune system gets overactive and attacks its healthy cells
- hipotiroidismo – low levels of thyroid hormones
- Nutrición pobre – deficiencies like vitamins B1, B6, and B12 deficiencies may lead you to polyneuropathy
- Trauma físico o lesión – injuries like accidents, etc. can cause polyneuropathy
- trauma ocupacional – repetitive motion of limbs e.g., typing, drilling can also damage your nerves by overworking them
Some people experience nerve damages in their body without any cause or risk factors. These cases are called polineuropatía idiopática.
Diagnóstico
Su médico confirmará un diagnóstico basado en su historial médico, examen médico y evaluación neurológica. Algunas pruebas sencillas para comprobar el sistema nervioso periférico sensoriomotor son las pruebas de reflejos, las pruebas de sensaciones, etc. Las pruebas de reflejos pueden incluir el reflejo de la rodilla, el reflejo del bíceps o del tríceps, etc. También se pueden evaluar otras pruebas de postura y marcha para ver si tiene estabilidad en la coordinación en sus movimientos sin tener un efecto adverso como dolor, etc.
Otras pruebas que pueden usarse para confirmar el diagnóstico de polineuropatía son:
- Electromiografía y pruebas de conducción nerviosa – these tests include sending of impulses in your muscles or nerves and measure the response to check the integrity of your nerves and muscles. These tests can also confirm the severity of the neuropathy that you have.
- Biopsias de nervio – biopsy refers to taking a live tissue as a sample and assessing it with different tests. These biopsies are taken to check if the cells are working properly.
- resonancia magnética o tomografía computarizada – these are imaging techniques through which the presence of underlying cause of neuropathy can be figured out. These causes can include tumours and herniated discs, etc.
- Análisis de sangre y muestras de orina. – the presence of abnormal blood components can hint towards some cause of polyneuropathy. For instance, high blood or urine sugar levels can indicate diabetic polyneuropathy, and the presence of auto-antibodies (antibodies against your own body) can be found in blood tests.
Tratamiento
Treatment of polyneuropathy depends on the symptoms you’re having and the severity of your symptoms. In patients who have an underlying disease-causing polyneuropathy e.g., diabetic patients, the underlying disease is treated with symptomatic medication for the associated problems. For idiopathic (due to an unknown reason) polyneuropathies, the usual treatment is to take care of the symptoms. Some of the available options are:
- medicamentos – medicines can help cure the underlying disease which is causing polyneuropathy. Insulin can be used to treat hyperglycaemia (high blood sugar levels) and thyroid hormones can be used to reverse polyneuropathy caused by hypothyroidism. Moreover, over-the-counter pain killers can be used to alleviate the pain caused by polyneuropathy
- Estimulación nerviosa eléctrica transcutánea – a gentle current is sent to the muscles or nerves by placing electrodes on the skin. This can help with the pain and extreme sensitivity
- Terapia de inmunoglobulina y plasmaféresis – these therapies aim to decrease the number of circulating autoantibodies in the body. This can reduce the destruction of nerve cells by your immune system. These therapies can be used to reduce the severity of polyneuropathy
- Terapia física – as with a lot of other musculoskeletal and nerve anomalies, physical therapy like massages, light active stretching, and exercises can help reduce pain, increase the mobility and overall strength of your muscles.
- Cirugía – Surgery is opted for cases of severe nerve compressions i.e., by a herniated disc or tumour
Complicaciones
Algunas complicaciones asociadas con la polineuropatía son:
- Úlceras o gangrena – occur especially in the feet and leg as a result of diabetic neuropathy. Infections in the lower limb can go unnoticed due to diminished sensations, causing ulcers and gangrene (tissue death). This can lead to amputation (cutting) of the limb. This condition is often referred to as diabetic foot/feet
- Caídas y lesiones – polyneuropathy can cause loss of fine control and you might become unstable leading to fall and injury
- Quemaduras y daños en la piel – inability to feel pain due to lack of sensation and lack of sensing temperature change can cause accidental burns
Prevención
La prevención de la polineuropatía incluye abordar los factores de riesgo que pueden causar esta afección. Puedes elegir:
- Avoid alcohol
- Evite el tabaco y el humo del cigarrillo.
- Avoid physical trauma by limiting repetitive tasks
- Eating a healthy and balanced diet
- tener una buena noche de sueño
- Additional types of neuropathy. (2013).
http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/neuropathy/additional-types-of-neuropathy.html - Autonomic neuropathy. (2013).
http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/neuropathy/autonomic-neuropathy.html
- Neuropatía (daño a los nervios). (Dakota del Norte).
http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/neuropathy/ - Diabetic neuropathy. (n.d.).
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/preventing-diabetes-problems/nerve-damage-diabetic-neuropathies - Peripheral neuropathy. (2018).
http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/neuropathy/peripheral-neuropathy.html - What is diabetic neuropathy? (2018).
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/nerve-damage-diabetic-neuropathies/what-is-diabetic-neuropathy
- polineuropatía By Miguel Rubin
MDCM, Hospital Presbiteriano de Nueva York-Centro Médico de Cornell
.
El contenido compartido en el sitio web de Health Literacy Hub se proporciona solo con fines informativos y no pretende reemplazar el consejo, el diagnóstico o el tratamiento ofrecido por profesionales médicos calificados en su estado o país. Se alienta a los lectores a confirmar la información provista con otras fuentes y buscar el consejo de un médico calificado con cualquier pregunta que puedan tener con respecto a su salud. Health Literacy Hub no es responsable de ninguna consecuencia directa o indirecta que surja de la aplicación del material proporcionado.