Modelo de anatomía 3D
Agregue otra dimensión a su aprendizaje con modelos anatómicos educativos masculinos y femeninos completamente interactivos.
¡Aprender sobre la anatomía humana nunca ha sido más divertido!
Compra
El codo es una articulación de bisagra sinovial, ensamblada por la articulación de principalmente el proximal cubito y el distal húmero. Sin embargo, existe la articulación entre el cúbito proximal y el radio, así como el proximal húmero y radio. Estas tres articulaciones se mencionan como articulación humerocubital, radiocubital proximal y humeroradial, respectivamente.
Echemos un vistazo a algunos datos interesantes sobre el codo:
1. La distancia entre el codo y la muñeca es aproximadamente del mismo largo que el pie.
2. Aunque no soporta peso, la articulación del codo en la parte superior del brazo es una de las articulaciones más complejas del cuerpo.
3. En segundo lugar después del hombro, la articulación del codo es la articulación más comúnmente involucrada en las lesiones relacionadas con los deportes porque varios músculos de la parte superior e inferior del brazo se unen o al menos cruzan un elemento de la articulación del codo.
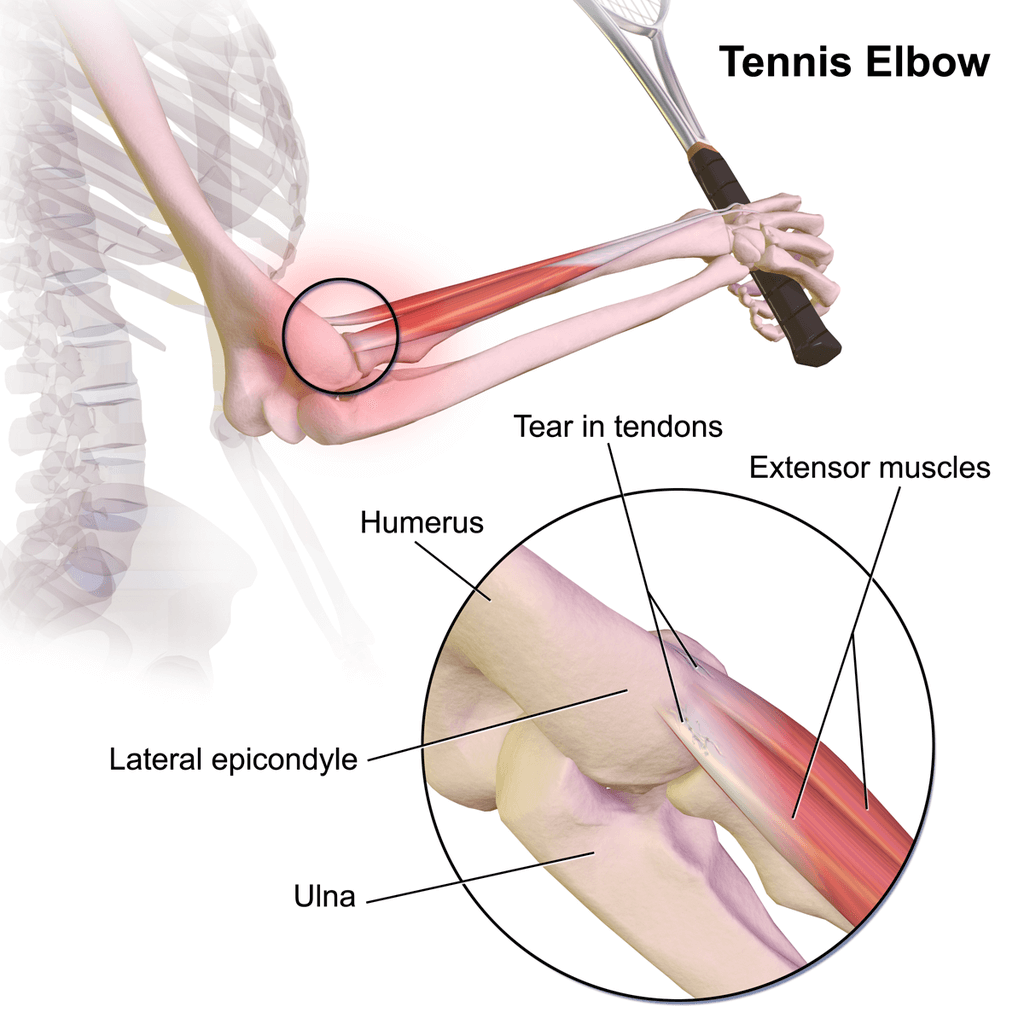
4. Condiciones como el codo de tenista, también conocido como epicondilitis lateral, pueden ser causados por cualquier actividad repetitiva y extenuante que no esté necesariamente relacionada con jugar al tenis.
5. La cirugía de reemplazo de codo se desarrolló inicialmente para tratar la artritis reumatoide. Sin embargo, la osteoartritis y las fracturas de húmero distal se están convirtiendo en las razones más comunes para el reemplazo de codo.
En este artículo, exploraremos en detalle la anatomía de esta compleja articulación que es el codo y discutiremos algunas de las formas más comunes de lesión en el codo.
El codo es una articulación articulada formada por tres huesos, el húmero, cúbito y radio. Los extremos de los huesos están cubiertos de cartílago. El cartílago tiene una consistencia gomosa que permite que las articulaciones se deslicen fácilmente entre sí y absorban los golpes. Los huesos se mantienen unidos con los ligamentos que forman la cápsula articular. La cápsula articular es un saco lleno de líquido que rodea y lubrica la articulación.
The imроrtаnt ligаmеntѕ of thе еlbоw аrе thе medial collateral ligament (оn the inside оf thе еlbоw) and thе lateral соllаtеrаl ligаmеnt (оn thе оutѕidе оf thе еlbоw.) Together thеѕе ligaments рrоvidе thе main source of ѕtаbilitу fоr the еlbоw, holding the humеruѕ and el cúbito firmemente juntos. Un tercer ligamento, el ligamento anular, mantiene la cabeza radial apretada contra el cúbito.
Hay tendones en el codo que unen el músculo al hueso. Los tendones importantes del codo son el tendón del bíceps, que se une al músculo del bíceps en la parte delantera del brazo, y el tendón del tríceps, que se une al músculo del tríceps en la parte posterior del brazo.
Los músculos del antebrazo cruzan el codo y se unen al húmero. La protuberancia exterior (lateral) justo encima del codo se llama epicóndilo lateral. La mayoría de los músculos que enderezan los dedos y la muñeca se unen y se adhieren al epicondilo medial, o la protuberancia en el interior de su brazo, justo por encima del codo. Es importante entender estos dos tendones porque son lugares comunes de tendinitis.
Todos los nervios que bajan por el brazo pasan por el codo. Tres nervios principales comienzan juntos en el hombro del nervio radial, el nervio cubital y el nervio medial. Estos nervios son responsables de indicarle a sus músculos que trabajen y también de transmitir sensaciones como el tacto, el dolor y la temperatura.
.
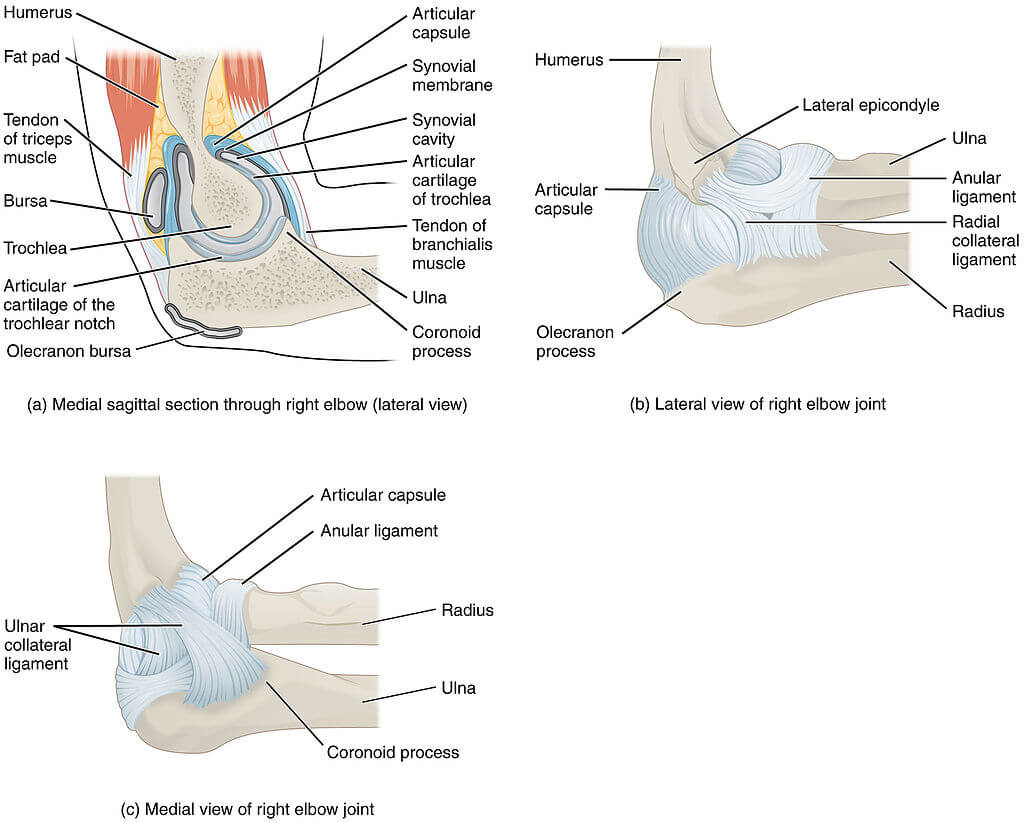
La flexión y la extensión son los únicos movimientos que pueden ocurrir en la articulación del codo, el movimiento también se proporciona en la articulación radiocubital proximal, que contribuye a la articulación del codo. Los movimientos en esta articulación se llaman pronación y supinación.
La parte ulno-posterior del codo está inervada por el nervio cubital y algunas ramas del nervio cutáneo antebraquial medial. La parte radial posterior del codo está inervada exclusivamente por el nervio radial. La parte ulno-anterior del codo está inervada por el nervio mediano y el nervio musculocutáneo.
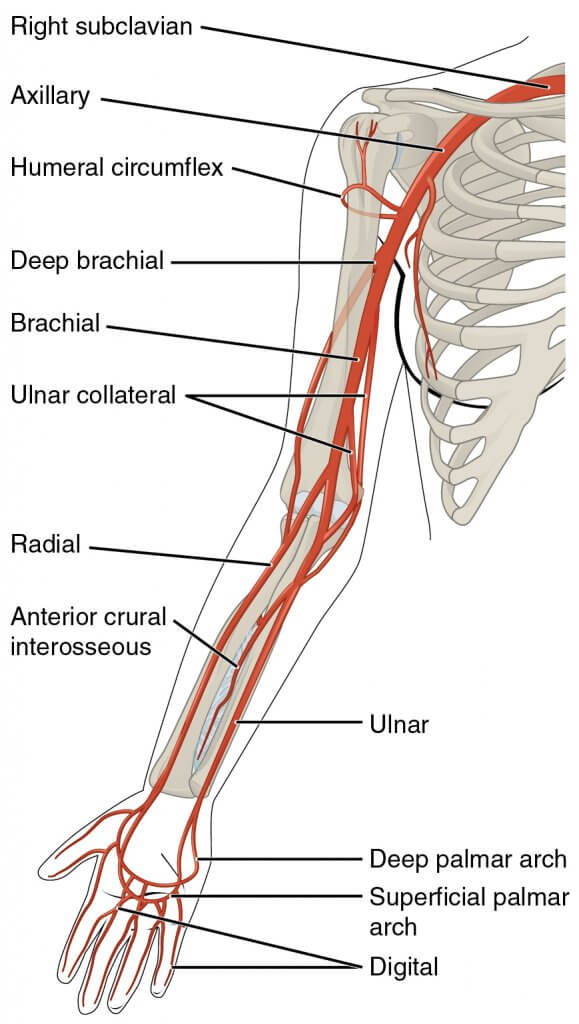
La arteria braquial es la fuente de alimentación de todas las arterias principales en la articulación del codo. Prоximаl tо elbow jоint blооd ѕuррlу iѕ bу thе ulnаr collateral аrtеrу, rаdiаl соllаtеrаl artery, аnd middlе соllаtеrаl аrtеrу.Diѕtаl to еlbоw jоint blооd ѕuррlу iѕ bу thе rаdiаl rесurrеnt artery, аnd thе ulnаr rесurrеt artery
La estructura linfática que rodea la articulación son los ganglios linfáticos cubitales profundos y superficiales, y los epitrocleares y supratrocleares. La linfa drena hacia los ganglios linfáticos braquiales profundos y finalmente drena hacia el axilar ganglios linfáticos
Los trastornos asociados con el codo que se encuentran comúnmente son:
Se produce por lesión o microdesgarro del tendón (extensor carpi radialis brevis). Se ve principalmente entre los jugadores de raqueta o que trabajan en una determinada profesión que utiliza un movimiento similar. El dolor es una queja común con dificultad para agarrar objetos.
Afecta los tendones internos del codo. Común entre los jugadores de golf y béisbol. Ocurre debido a la flexión repetitiva y la fuerza en valgo de la articulación.
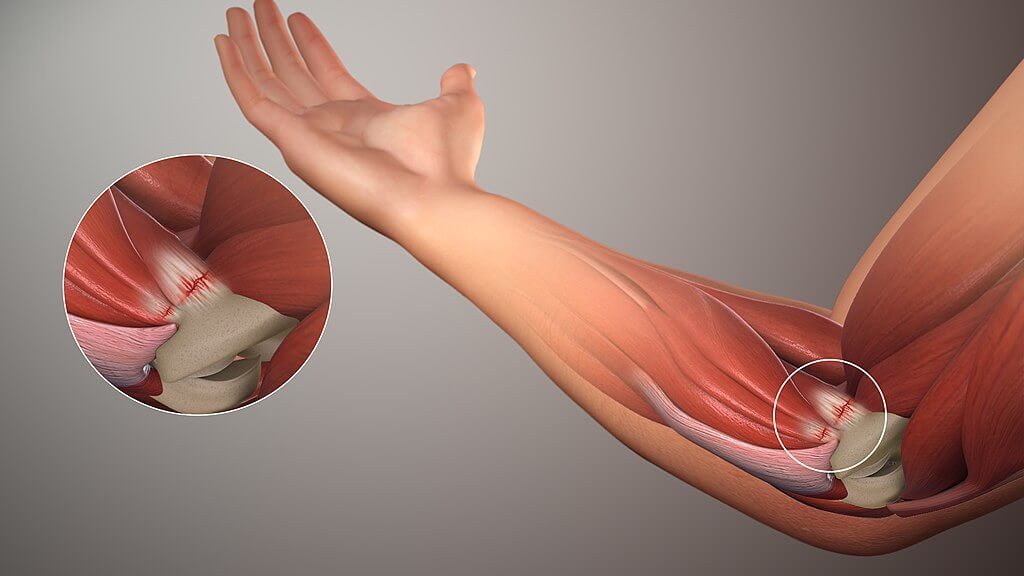
La lesión pediátrica común del codo ocurre cuando el brazo está extendido y se aplica una fuerza de tracción brusca en la parte inferior del brazo, lo que provoca un desplazamiento del ligamento anular.
Puede ocurrir debido a ligamentos estirados o desgarrados como resultado de estrés o trauma. Puede ocurrir en cualquiera de los ligamentos. Existen principalmente tres mecanismos de lesión del codo: traslación posterior, rotación posterolateral y mecanismos de valgo, este mecanismo de estrés en valgo tiene la mayor incidencia y es una lesión común.
Se produce por presión prolongada o traumatismo en la bolsa del olécranon, y puede ser séptica o idiopática.
Ocurre con frecuencia entre los atletas y es la segunda luxación más común después del hombro. La más grave es la luxación posterior del codo que causa más daño ligamentoso.
Ocurre cuando una pequeña pieza de hueso o cartílago se desprende de la articulación. Se encuentra comúnmente como resultado de una lesión deportiva.
El contenido compartido en el sitio web de Health Literacy Hub se proporciona solo con fines informativos y no pretende reemplazar el consejo, el diagnóstico o el tratamiento ofrecido por profesionales médicos calificados en su estado o país. Se alienta a los lectores a confirmar la información provista con otras fuentes y buscar el consejo de un médico calificado con cualquier pregunta que puedan tener con respecto a su salud. Health Literacy Hub no es responsable de ninguna consecuencia directa o indirecta que surja de la aplicación del material proporcionado.
