3डी एनाटॉमी मॉडल
पूरी तरह से इंटरैक्टिव शैक्षिक पुरुष और महिला शारीरिक मॉडल के साथ अपने सीखने में एक और आयाम जोड़ें।
मानव शरीर रचना के बारे में सीखना इतना मजेदार कभी नहीं रहा!
खरीदना
The human brain is a very sensitive structure in terms of trauma and injury. Several protective features help keep the brain in a protective environment. One of these features is the meninges.
आइए एक नजर डालते हैं मेनिन्जेस के बारे में सबसे दिलचस्प तथ्यों पर।
1. The meninges are sheet-like covering of the brain that help keep the Central Nervous System ( CNS ) in place and stabilise it. The meninges are also found within the spinal canal in the spinal cord.
2. मस्तिष्क और रीढ़ में, मेनिन्जेस मस्तिष्कमेरु द्रव (सीएसएफ) के संचलन को भी नियंत्रित करता है जो तंत्रिका ऊतक को सुरक्षा और पोषक तत्व प्रदान करता है।
3. Specialised cells (meningeal cells) in the meningeal tissue are responsible for a protective mechanism called meningeal immunity that controls and intervene in the presence of a pathogen-mediated infection.
4. What we refer to as “the meninges” represents three independent layers of tissue located in the skull (cranial cavity) and surrounding the spinal cord characterised by a unique structure and role. The dura mater, the outermost layer, consists of two sheets of connective tissue lining the interior surface of the cranial cavity. The arachnoid layer, the middle layer, is made of non-vascularised connective tissue. The pia mater, the innermost layer, is a very thin sheet that covers the brain surface and is highly vascularised.
5. The space between the arachnoid and pia maters is known as “subarachnoid space”. In this region where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates, there is a particular compartment (subarachnoid cisterns) characterised by the accumulation of CSF (pools or cisterns) to provide the brain with nutrients, enable solute exchange, and offer mechanical and functional support to the brain.
इस लेख में, हम इस मस्तिष्क-सुरक्षात्मक परत से जुड़ी संरचना, कार्य और सबसे आम बीमारियों पर विस्तार से चर्चा करेंगे।
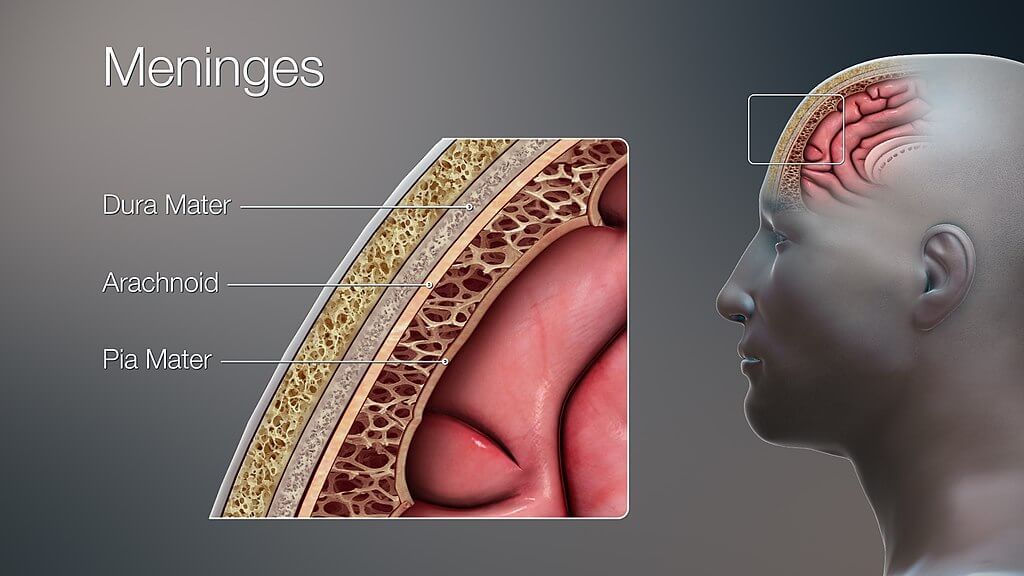
Our brain is suspended or floating in the CSF and covered by तीन मेनिन्जेस की परतें:
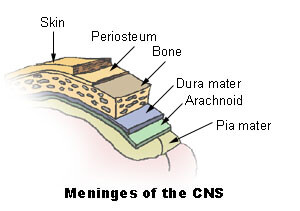
मेनिन्जेस मस्तिष्क और रीढ़ की हड्डी दोनों को ढंकते हैं और उन्हें अपने आसपास की हड्डियों यानी खोपड़ी और कशेरुक स्तंभ से अलग करते हैं। मेनिन्जेस को आगे स्थलाकृतिक रूप से वर्गीकृत किया गया है कपाल तथा रीढ़ की हड्डी में meninges. There are three clinically important spaces bounded by the meninges, they are the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. The arachnoid and मृदुतानिका भी कहा जाता है लेप्टोमेनिंग्स; इसका कारण इन दो परतों के बीच सीएसएफ की मौजूदगी है।
Apart from its mechanical function, the meninges act to support the blood vessels and form a continuous cavity for the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
The ड्यूरा मैटर सबसे बाहरी मेनिन्जियल परत है। इसमें घने अनियमित संयोजी ऊतक होते हैं और यह दो परतों से बना होता है:
These two layers are inseparable except in places where they separate to envelop large veins known as dural venous sinuses. In these above-mentioned places, the ड्यूरा मैटर projects inward towards the brain tissue forming a fibrous partition. These partitions are within the कपाल और इस प्रकार हैं:
रीढ़ की हड्डी का हिस्सा ड्यूरा मैटर इसके विपरीत पेरीओस्टियल परत नहीं होती है। इस अंतर को इस तथ्य के लिए जिम्मेदार ठहराया जा सकता है कि खोपड़ी के विपरीत कशेरुक स्तंभ की अपनी पेरीओस्टियल परत होती है।
मेनिन्जेस की यह परत ड्यूरा और . के बीच सैंडविच होती है मृदुतानिका. क्षमता ड्यूरा और अरचनोइड मेटर के बीच की जगह को कहा जाता है अवदृढ़तानिकी (ड्यूरा से गहरा) और अरचनोइड और . के बीच की जगह मृदुतानिका कहा जाता है अवजालतनिका (deeper to arachnoid) space. The latter is a true space that contains the Cerebrospinal fluid in it. This space is also the location of all the cerebral arteries and veins. The रीढ़ की हड्डी में अरचनोइड पदार्थ कपाल अरचनोइड मेटर की निरंतरता है।
अरचनोइड ड्यूरा से जुड़ा हुआ है और मृदुतानिका अलग-अलग जगहों पर। ड्यूरा पदार्थ के साथ लगाव के स्थान पर मशरूम जैसे उभार होते हैं जिन्हें कहा जाता है मकड़ी का ग्रेनुलेशन. These granulations protrude into the dural venous sinuses and enable the continuous flow of CSF from the subarachnoid space to the venous system.
यह एक पतली, अत्यधिक संवहनी परत है जो मस्तिष्क की आकृति का बारीकी से अनुसरण करती है। मस्तिष्क की कुछ वाहिकाएं इस परत से संबंधित होती हैं लेकिन वे इसमें अंतर्निहित होती हैं मृदुतानिका और अलग से नाम नहीं है। मृदुतानिका functions to physically separate the nervous tissue from the vasculature present in the subarachnoid space. It also increases the efficacy of the blood-brain barrier, a vital component for the brain tissue to stay healthy.
रीढ़ की हड्डी मृदुतानिका closely attaches to the spinal cord and gives off a fibrous projection at the end of the spinal cord – the फिल्म टर्मिनल।
जैसा कि पहले बताया गया है कि तीन मेनिन्जियल परतों के बीच संभावित स्थान होते हैं और वे इस प्रकार हैं:
These spaces are of much clinical importance in traumatic injuries to the head. Blood can leak into these spaces pathologically and cause haemorrhages which can be fatal.
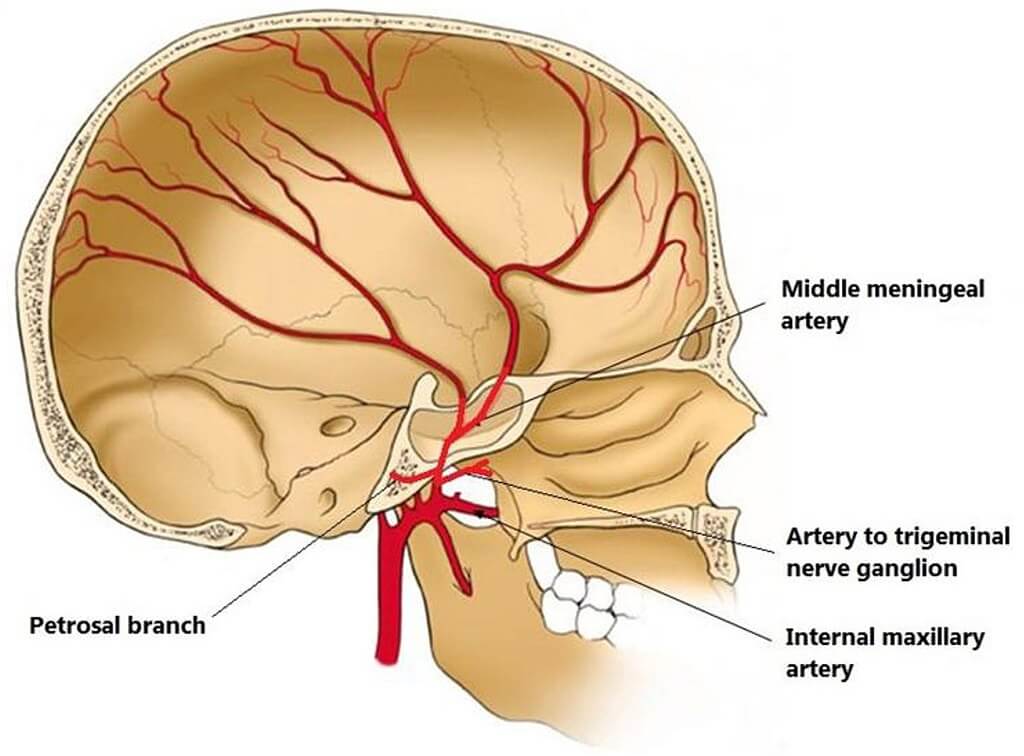
मेनिन्जेस को द्वारा संक्रमित किया जाता है त्रिधारा तंत्रिका (Fifth cranial nerve). The blood supply to the meninges is from the branches of the कैरोटिड तथा हड्डीवाला धमनियां।
The सूजन (swelling) of the meninges is termed मस्तिष्कावरण शोथ. यह आमतौर पर बैक्टीरिया के कारण होता है लेकिन वायरस के कारण हो सकता है और यहां तक कि दवा से प्रेरित भी होता है। बैक्टीरियल मेनिनजाइटिस आमतौर पर दो बग (रोगजनकों) के कारण होता है: नेइसेरिया मेनिन्जाइटिडिस तथा स्ट्रैपटोकोकस निमोनिया. दूसरी ओर, वायरल मैनिंजाइटिस, सबसे अधिक किसके कारण होता है? एंटरोवायरस.
मस्तिष्कावरण शोथ आमतौर पर कारण की पुष्टि के बाद एंटीबायोटिक्स और एंटीवायरल दवा द्वारा इलाज किया जाता है। अनुपचारित में, हालांकि, गंभीर जटिलताओं की ओर बढ़ सकता है जैसे, brain herniations, आदि।
मेनिन्जाइटिस के बारे में और जानें यह लेख।
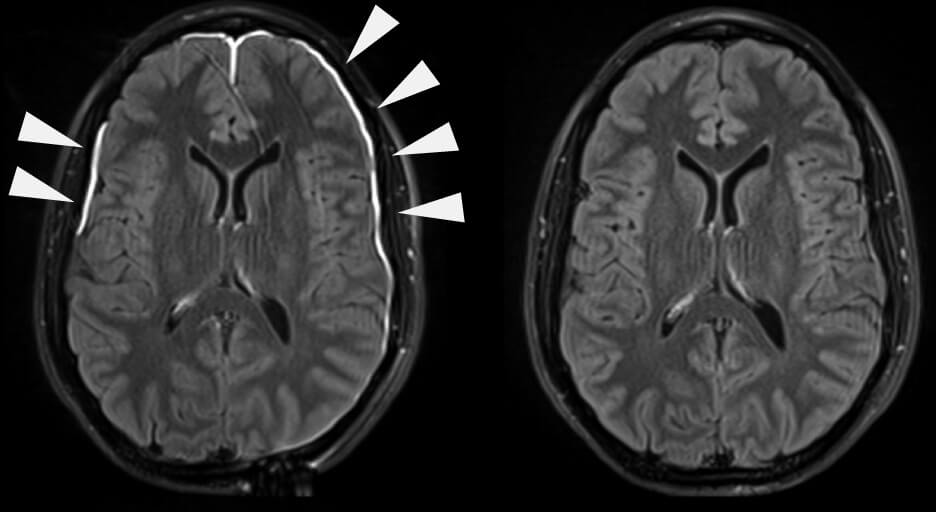
ए रक्तगुल्म is blood pooling or collection. Increased pressure in the skull due to this build-up causes a rapid increase in the intracranial pressure due to the skull being a closed cavity. On CT scans they are seen as crescent-shaped formations. There are two types of haematomas:
Another classification of subdural haematomas is based on the timeframe of their formation i.e., acute or chronic subdural haematomas. Acute haematomas are caused by sudden forceful brain injuries while chronic haematomas can result from a weak or small injury and are usually due to another underlying cause. Haematomas can be fatal if they are not treated immediately.
हेल्थ लिटरेसी हब वेबसाइट में साझा की गई सामग्री केवल सूचना के उद्देश्यों के लिए प्रदान की जाती है और इसका उद्देश्य आपके राज्य या देश में योग्य चिकित्सा पेशेवरों द्वारा दी जाने वाली सलाह, निदान या उपचार को प्रतिस्थापित करना नहीं है। पाठकों को अन्य स्रोतों के साथ प्रदान की गई जानकारी की पुष्टि करने और अपने स्वास्थ्य के संबंध में किसी भी प्रश्न के लिए एक योग्य चिकित्सक की सलाह लेने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया जाता है। स्वास्थ्य साक्षरता हब प्रदान की गई सामग्री के उपयोग से उत्पन्न होने वाले किसी भी प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष परिणाम के लिए उत्तरदायी नहीं है।
